| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
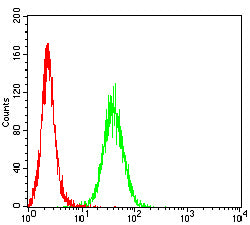
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
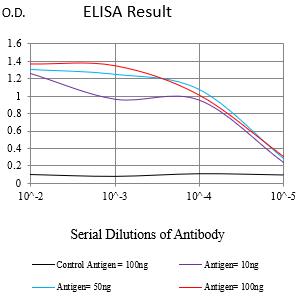
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SELP; CD62; GRMP; PSEL; GMP140; LECAM3; PADGEM |
| Entrez GeneID | 6403 |
| clone | 7A3D9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 90.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD62P (AA: extra 42-208) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与C4A抗体相关的代表性文献,内容涵盖其在自身免疫疾病中的作用机制和临床研究:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Genetic deficiency of C4A is a major risk factor for systemic lupus erythematosus"*
**作者**: Hauptmann G, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过分析系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者群体,发现C4A基因的缺失与SLE发病风险显著相关。C4A蛋白的缺乏可能导致补体系统异常激活,促进自身抗体(如抗dsDNA抗体)的产生和免疫复合物清除障碍。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"C4A copy number variations in autoimmune diseases: Association with systemic lupus erythematosus and primary Sjögren’s syndrome"*
**作者**: Yu CY, et al.
**摘要**: 研究探讨了C4A基因拷贝数变异与自身免疫疾病的关系,发现低C4A拷贝数患者更易出现抗Ro/SSA和抗La/SSB抗体阳性,提示C4A缺陷可能通过影响免疫耐受导致自身抗体产生。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Anti-C4A antibodies in COVID-19: A potential link to complement-mediated thrombotic microangiopathy"*
**作者**: Daha NA, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了COVID-19重症患者中抗C4A抗体的异常升高,并发现其与补体过度激活和血栓性微血管病变相关,为C4A抗体在感染性疾病中的病理作用提供了新证据。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"C4d-specific monoclonal antibodies detect pathologic immune complexes in lupus nephritis"*
**作者**: Aggarwal R, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了靶向补体C4d片段的单克隆抗体,用于检测SLE患者肾组织中的免疫复合物沉积,证实C4裂解产物(如C4d)可作为狼疮肾炎的生物标志物,间接反映了C4A异常在疾病中的作用。
---
**注**:C4A研究多聚焦于基因缺失或表达异常,直接针对“抗C4A抗体”的研究较少,部分文献需结合补体系统(如C4d)相关病理机制间接分析。建议通过PubMed/Google Scholar以关键词“C4A antibody”或“anti-C4A”获取最新进展。
C4A antibodies target the C4A isoform of complement component 4 (C4), a critical protein in the classical and lectin pathways of the complement system. C4 exists as two major isoforms, C4A and C4B, encoded by highly homologous genes within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region. While both isoforms participate in pathogen clearance and immune complex processing, C4A preferentially binds amino groups, facilitating covalent attachment to immune complexes, whereas C4B reacts with hydroxyl groups, enhancing microbial opsonization.
C4A deficiency or dysfunction, often linked to gene copy number variations or mutations, is associated with autoimmune disorders, particularly systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Autoantibodies against C4A may arise in autoimmune contexts, potentially exacerbating complement dysregulation. These antibodies can interfere with C4A’s role in immune complex clearance, contributing to tissue inflammation and organ damage. Additionally, C4A autoantibodies have been implicated in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and schizophrenia, though mechanisms remain under investigation.
Research on C4A antibodies focuses on their diagnostic and prognostic value. In SLE, anti-C4A antibodies correlate with disease activity and renal involvement. Their detection may aid in stratifying patients or monitoring treatment responses. However, standardization of assays and clearer pathophysiological insights are needed for clinical translation. Studies also explore genetic-epigenetic interactions influencing C4A expression and autoantibody production, offering potential therapeutic targets. Overall, C4A antibodies represent both biomarkers and mechanistic players in complement-related pathologies.
×