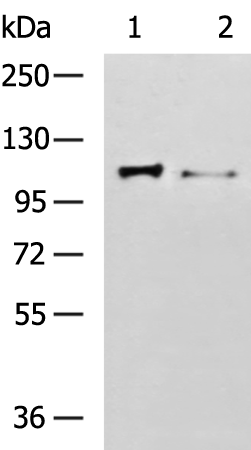
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
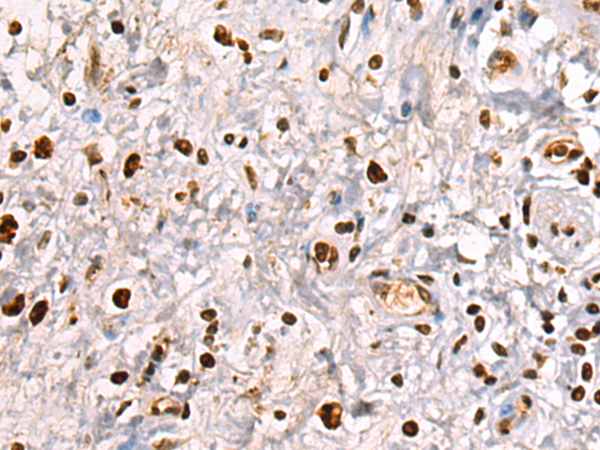
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | TOPI |
| WB Predicted band size | 91 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human TOP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TOP1抗体(抗拓扑异构酶I抗体)的3篇代表性文献,简要总结如下:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies to Topoisomerase I in Systemic Sclerosis*
**作者**: J.R. McNeely, M.J. Fritzler, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究证实抗TOP1抗体(Scl-70抗体)是系统性硬化症(硬皮病)的特异性血清标志物,尤其与弥漫性皮肤型硬皮病相关,并探讨了其在疾病诊断和预后评估中的作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Comparison of ELISA and Immunoprecipitation for Detecting Anti-Topoisomerase I Antibodies*
**作者**: G. Marguerite, P.J.W. Venables
**摘要**: 研究比较了ELISA和免疫沉淀法检测抗TOP1抗体的敏感性和特异性,指出ELISA更适合临床筛查,而免疫沉淀法在确认高特异性诊断中的价值。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Clinical Utility of Anti-Topoisomerase I Antibody Testing in Connective Tissue Diseases*
**作者**: A.M. Spencer-Green, R.W. Simms
**摘要**: 分析了抗TOP1抗体在多种结缔组织病中的分布,强调其与肺部纤维化、肾脏受累等系统性硬化症并发症的关联,并讨论了抗体滴度与疾病活动度的关系。
---
以上文献均聚焦于抗TOP1抗体的临床意义、检测方法及其在自身免疫病中的病理机制研究。
TOP1 antibody, also known as anti-topoisomerase I antibody or anti-Scl-70. is a highly specific autoantibody associated with autoimmune disorders, particularly systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Topoisomerase I (TOP1) is a nuclear enzyme that regulates DNA topology during replication and transcription by transiently cleaving and rejoining DNA strands. In autoimmune contexts, TOP1 becomes a target of the immune system, leading to antibody production.
First identified in the 1980s, TOP1 antibodies are most strongly linked to diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc), a subtype characterized by rapid skin thickening and internal organ involvement. Approximately 20-30% of systemic sclerosis patients test positive for these antibodies, which serve as a diagnostic marker and prognostic indicator. Their presence correlates with increased risk of pulmonary fibrosis, cardiac complications, and reduced survival rates compared to other autoantibody profiles.
Detection typically employs ELISA or immunoblotting using recombinant TOP1 antigens. While pathogenic mechanisms remain partially understood, TOP1 antibodies may contribute to tissue damage through molecular mimicry or immune complex deposition. Recent studies also explore their potential role in cancer biology, as TOP1 is a target for chemotherapeutic agents like irinotecan. In oncology, TOP1 antibody levels might influence treatment responses or serve as paraneoplastic markers, though this requires further validation. Research continues to investigate epitope specificity and clinical utility across autoimmune and malignant conditions.
×