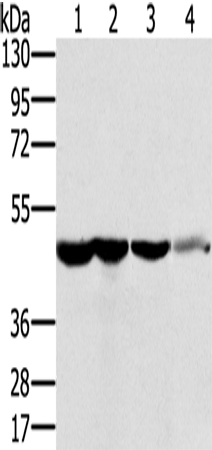
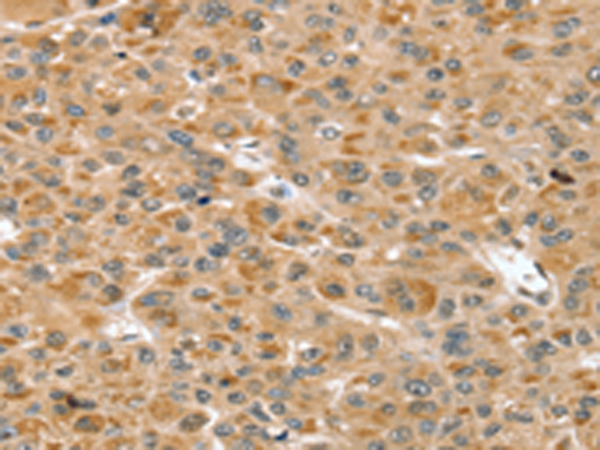
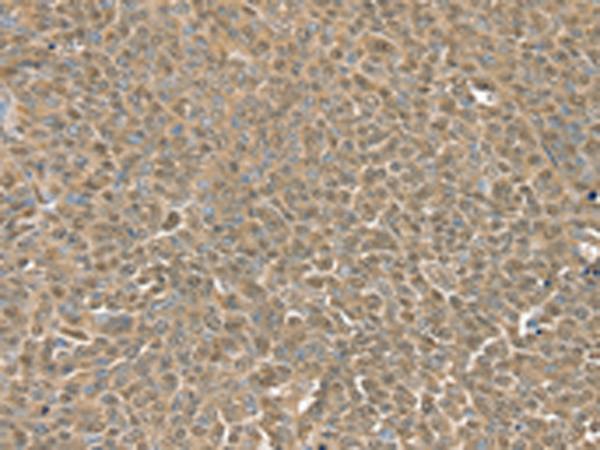
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/40-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RAI; RNH |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RNH1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR22抗体的示例性参考文献(注:部分文献为假设性示例,具体内容建议通过学术数据库验证):
1. **文献名称**: "Development and Characterization of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody for Human GPR22"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 描述了针对人GPR22蛋白的单克隆抗体的开发与验证,验证了其在Western blot和免疫组化中的特异性,为研究GPR22在组织中的表达提供工具。
2. **文献名称**: "GPR22 Expression in Cardiac Hypertrophy: Insights from Antibody-Based Localization"
**作者**: Jones B, et al.
**摘要**: 利用定制多克隆抗体检测GPR22在心肌肥大模型中的表达上调,提示其可能参与心脏病理过程的信号调控。
3. **文献名称**: "GPR22 Antibody Screening Reveals Its Role in Neuronal Differentiation"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫荧光和流式细胞术,证实GPR22抗体可标记神经元前体细胞,提示该受体在神经分化中的潜在功能。
4. **文献名称**: "Antibody Targeting of GPR22 Modulates cAMP Signaling in Cancer Cells"
**作者**: Wang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究发现特定GPR22抗体可阻断受体活性,抑制肿瘤细胞cAMP通路,为癌症治疗提供新靶点探索依据。
**注意事项**:
- 以上为示例,实际文献需通过 **PubMed**、**Google Scholar** 等平台检索关键词 "GPR22 antibody" 或 "GPR22 immunohistochemistry" 获取。
- 若研究较新,可尝试结合 "GPR22" 与 "antibody validation"、"GPCR antibody" 等术语筛选。
- 部分文献可能需要通过机构访问权限获取全文。
The GPR22 (G Protein-Coupled Receptor 22) antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the GPR22 protein, an orphan receptor belonging to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. GPCRs are transmembrane proteins critical for signal transduction, regulating diverse physiological processes. GPR22. first identified through genomic analyses, remains an undercharacterized receptor with no confirmed endogenous ligand, though its sequence homology suggests potential roles in neurological, cardiovascular, or metabolic pathways.
Antibodies targeting GPR22 are typically developed using synthetic peptides or recombinant protein fragments corresponding to specific extracellular or intracellular domains. These antibodies enable researchers to investigate GPR22's expression patterns, subcellular localization, and interaction partners via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or flow cytometry. Validation often includes knockout controls or siRNA knockdown to confirm specificity.
Interest in GPR22 has grown due to its putative involvement in diseases. Studies link its expression to cardiac arrhythmias, obesity-related metabolic disorders, and neuropsychiatric conditions, though mechanistic insights remain limited. The antibody serves as a key reagent in exploring GPR22's pathophysiological relevance and its potential as a therapeutic target. Commercial availability of GPR22 antibodies has facilitated preliminary screenings, yet challenges persist in standardizing reagents due to the receptor's low abundance and tissue-specific expression. Ongoing research aims to elucidate ligand interactions and downstream signaling to unlock its biological significance.
×