| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
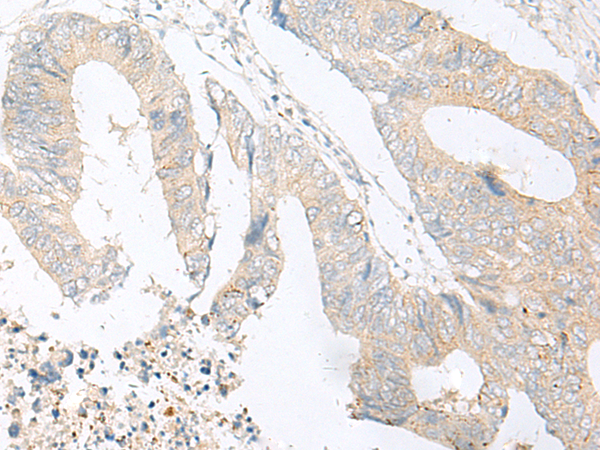
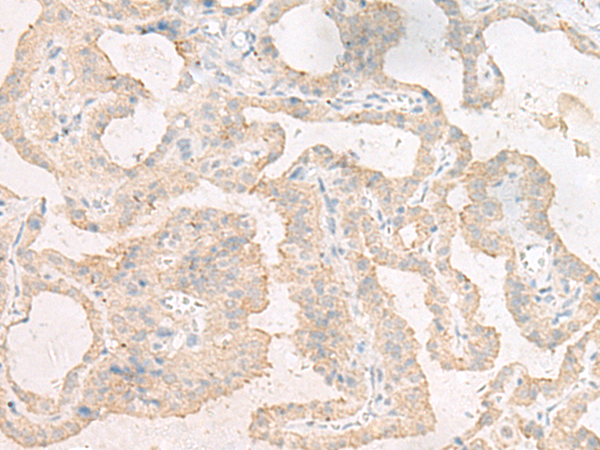
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GOAT; OACT4; FKSG89 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MBOAT4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与MBOAT4(LPIAT1)抗体相关的文献,简要概括其研究内容:
1. **文献名称**: *"LPIAT1 regulates arachidonic acid content in phosphatidylinositol and is required for cortical lamination in mice"*
**作者**: Lee HC et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用MBOAT4/LPIAT1特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化证实该酶在小鼠大脑皮层发育中调控磷脂酰肌醇中的花生四烯酸水平,并揭示其缺失导致神经元迁移障碍。
2. **文献名称**: *"Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase family member 4 (MBOAT4) is a potential therapeutic target for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease"*
**作者**: Meroni M et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用抗MBOAT4抗体),发现MBOAT4在肝脏脂代谢中的作用,其表达水平与人类非酒精性脂肪肝(NAFLD)的严重程度呈负相关。
3. **文献名称**: *"Genetic and functional characterization of MBOAT4 variants in inflammatory bowel disease"*
**作者**: Sazonovs A et al.
**摘要**: 通过基因关联分析结合免疫沉淀实验(使用MBOAT4抗体),发现MBOAT4基因变异可能通过影响肠上皮细胞膜的磷脂重塑,参与炎症性肠病(IBD)的发病机制。
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词"MBOAT4 antibody"+"LPIAT1"+"function"核实具体文献。
Membrane-bound O-acyltransferase domain-containing 4 (MBOAT4), also known as lysophosphatidylserine acyltransferase 1 (LPSAT1), is an enzyme involved in lipid metabolism, specifically catalyzing the transfer of acyl groups to lysophosphatidylserine to form phosphatidylserine. This process is critical for maintaining membrane phospholipid composition and cellular signaling. Dysregulation of MBOAT4 has been implicated in metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer, making it a subject of growing research interest.
Antibodies targeting MBOAT4 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional roles. These antibodies are typically developed using immunogens derived from conserved regions of the human MBOAT4 protein and validated through techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Specificity is confirmed using knockout cell lines or tissues. Researchers employ MBOAT4 antibodies to investigate its tissue distribution, particularly in the liver, brain, and adipose tissue, as well as its altered expression in pathological conditions such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or glioblastoma. Additionally, these antibodies aid in exploring MBOAT4's interaction networks and regulatory mechanisms in lipid homeostasis. Recent studies also assess its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker, driving demand for reliable detection reagents. Commercial MBOAT4 antibodies often include validation data to ensure reproducibility across experimental models.
×