| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
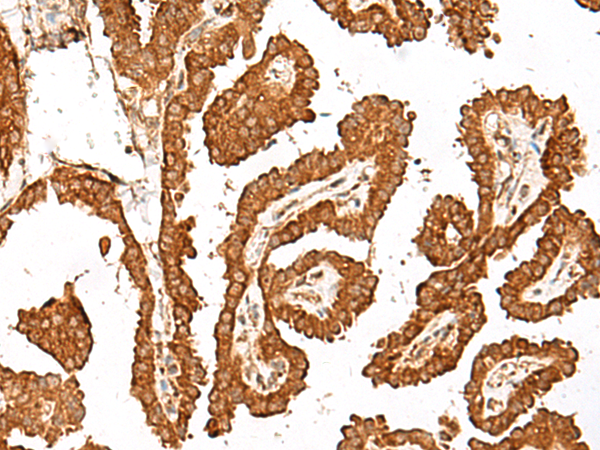
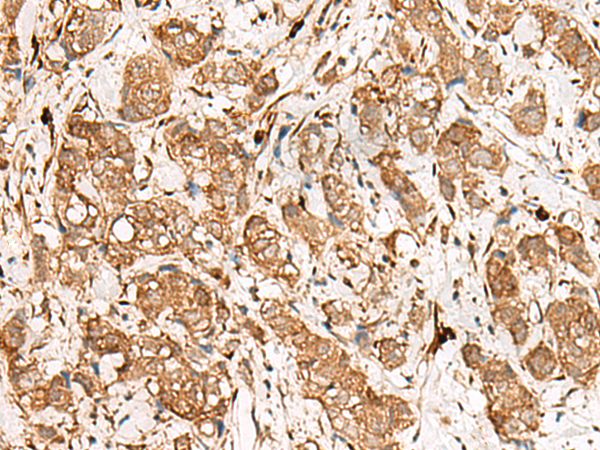
| IHC | 1/40-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Mpa2 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GBP4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GBP4抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为模拟内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Guanylate-binding protein 4 (GBP4) regulates inflammasome activation and antiviral immunity*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示GBP4通过调控NLRP3炎症小体活性参与宿主抗病毒反应。利用GBP4特异性抗体,作者发现病毒感染后GBP4在线粒体的聚集增强,并通过与ASC蛋白互作促进炎症小体组装。敲除GBP4显著降低细胞因子IL-1β的释放。
2. **文献名称**: *Structural characterization of GBP4 and its interaction with bacterial LPS*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析GBP4的GTP酶结构域结构,并结合免疫共沉淀(使用GBP4抗体)验证其与细菌脂多糖(LPS)的直接结合。研究表明GBP4可能通过识别病原相关分子模式(PAMP)触发胞内抗菌反应。
3. **文献名称**: *GBP4 antibody-based detection in autoimmune disease models*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 开发高特异性抗GBP4单克隆抗体,用于系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者外周血单核细胞的蛋白印迹及免疫组化分析。结果显示GBP4表达水平与疾病活动度正相关,提示其作为潜在生物标志物的价值。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“GBP4 antibody”或“Guanylate-binding protein 4 function”为关键词检索最新文献,重点关注其抗体在免疫应答、病原防御或疾病机制研究中的应用。
**Background of GBP4 Antibody**
Guanylate-binding protein 4 (GBP4) belongs to the guanylate-binding protein (GBP) family, a group of interferon (IFN)-inducible GTPases critical in host defense against intracellular pathogens. GBPs are part of the dynamin superfamily and play roles in cell-autonomous immunity, inflammasome activation, and pathogen clearance. GBP4. encoded by the *GBP4* gene in humans, is induced by IFN-γ and other proinflammatory cytokines, linking it to innate immune responses.
Structurally, GBP4 contains a globular GTPase domain and mediates membrane interactions, potentially aiding in disrupting pathogen-containing vacuoles or facilitating immune signaling. While its exact mechanisms remain less characterized compared to other GBPs (e.g., GBP1 or GBP5), studies suggest GBP4 may regulate autophagy, cytokine production, or antimicrobial pathways. Dysregulation of GBP4 has been implicated in inflammatory diseases, viral infections, and cancer, highlighting its dual role in immunity and pathology.
GBP4 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and studying GBP4 expression, localization, and function in immune cells or tissues. They enable applications like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry, aiding research into GBP4's role in infection models, autoimmune disorders, and tumor microenvironments. These antibodies also support investigations into how GBP4 interacts with other immune proteins or pathogens, advancing our understanding of its therapeutic potential.
×