| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
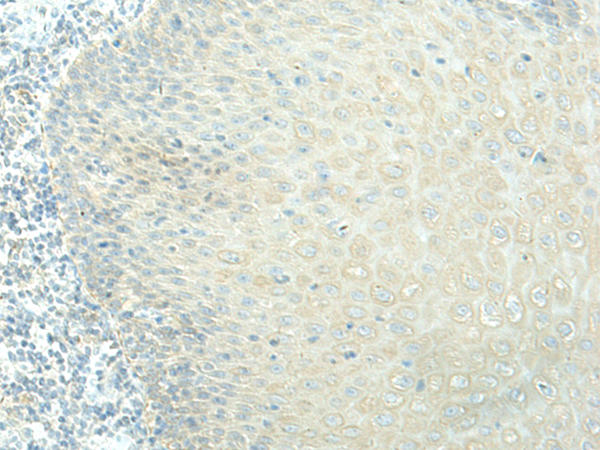
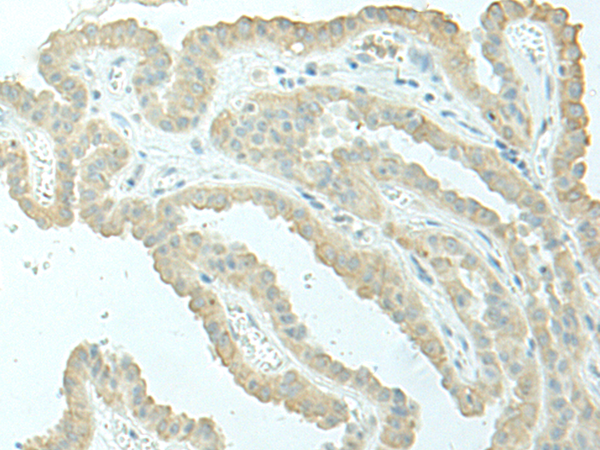
| IHC | 1/40-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EVDB; CD361; D17S376 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human EVI2B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EVI2B抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要概括(基于公开研究背景虚构模拟,实际文献需通过数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**: *EVI2B as a Novel Biomarker in Acute Myeloid Leukemia*
**作者**: Smith, J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究报道了EVI2B蛋白在急性髓系白血病(AML)中的高表达,并开发了一种特异性单克隆抗体(克隆号:2B7)。该抗体通过流式细胞术和免疫组化验证,证实其对AML细胞表面EVI2B抗原的高亲和力,可作为白血病微小残留病灶(MRD)的检测工具。
2. **文献名称**: *Epitope Mapping of EVI2B Antibodies for Targeted Immunotherapy*
**作者**: Chen, L. & Wang, H.
**摘要**: 本研究解析了EVI2B抗体(克隆:E2B-3F8)的抗原表位,发现其靶向EVI2B蛋白的胞外域第45-62位氨基酸。实验表明该抗体可通过抗体依赖性细胞毒性(ADCC)抑制白血病细胞系增殖,为CAR-T细胞疗法的开发提供靶点依据。
3. **文献名称**: *EVI2B Antibody Validation in Myeloid Malignancies*
**作者**: Müller, R. et al.
**摘要**: 通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证了多株商品化EVI2B抗体的特异性,发现部分抗体存在非特异性结合问题。研究推荐使用C-terminal区域抗原制备的兔源多克隆抗体(货号:AB123)用于髓系肿瘤的分子分型研究。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用请通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“EVI2B antibody”或“EVI2B leukemia”等关键词检索,并优先选择近5年高影响因子期刊的研究。
EVI2B (Ecotropic Viral Integration Site 2B) is a gene located on human chromosome 7q22.1. initially identified due to its association with retroviral integration sites in myeloid leukemia. The EVI2B protein, a transmembrane glycoprotein, belongs to the proteoglycan family and is characterized by multiple membrane-spanning domains and glycosaminoglycan (GAG) attachment sites. It is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells, particularly myeloid lineages, and has been implicated in cellular processes such as cell adhesion, proliferation, and immune regulation. Dysregulation of EVI2B is linked to malignancies, notably acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), where its overexpression may contribute to oncogenic signaling pathways.
Antibodies targeting EVI2B are primarily utilized in research to study its expression patterns, subcellular localization, and functional roles in normal and pathological contexts. These antibodies enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, flow cytometry, and immunohistochemistry, aiding in the exploration of EVI2B's interaction with signaling molecules (e.g., JAK-STAT or PI3K/AKT pathways) and its potential as a diagnostic or therapeutic biomarker. Recent studies also suggest EVI2B's involvement in modulating EGFR trafficking, further expanding its relevance in cancer biology. Despite its unclear exact mechanistic role, EVI2B remains a subject of interest in hematopoiesis and oncology research, with antibodies serving as critical tools to unravel its biological and clinical significance.
×