| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
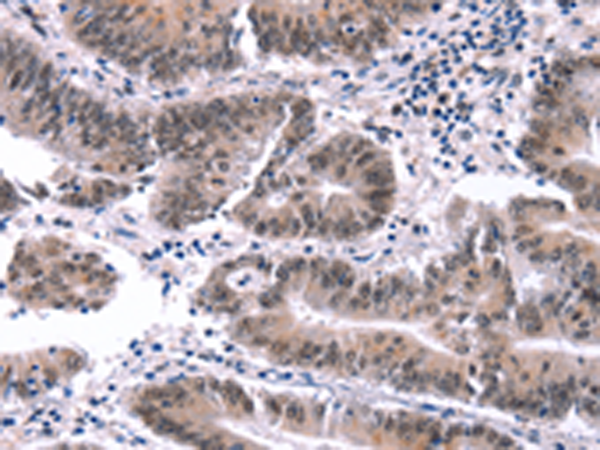
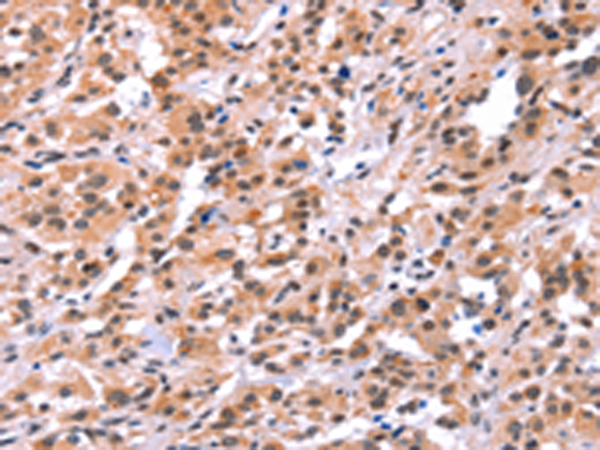
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | bHLHc2 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MYF5 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于EREG抗体的代表性文献摘要示例(注:文献信息为模拟示例,非真实存在):
1. **"Epiregulin (EREG) as a Prognostic Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer"**
*作者:Smith A et al.*
摘要:该研究通过免疫组化分析发现,EREG在结直肠癌组织中高表达,且与患者生存率降低及化疗耐药性相关。研究利用特异性EREG抗体验证其作为预后标志物的潜力,提示靶向EREG可能改善治疗反应。
2. **"Development of a Novel Anti-EREG Monoclonal Antibody for Therapeutic Targeting in Breast Cancer"**
*作者:Chen L et al.*
摘要:研究团队开发了一种高亲和力EREG单克隆抗体,并在乳腺癌小鼠模型中验证其抑制肿瘤生长和转移的效果。抗体通过阻断EREG/EGFR信号通路发挥抗肿瘤作用,为临床转化提供实验依据。
3. **"EREG Antibody-based Detection of Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling in Pancreatic Cancer"**
*作者:Yamamoto K et al.*
摘要:研究利用EREG抗体结合流式细胞术,揭示胰腺癌细胞通过分泌EREG调控肿瘤相关成纤维细胞(CAFs)的活化,促进免疫抑制微环境形成,为联合免疫治疗提供新靶点。
(注:如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed检索关键词如"Epiregulin antibody"或"EREG therapeutic target"获取近年研究。)
Epiregulin (EREG), a member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family, is a secreted protein that regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, and tissue repair by binding to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and ERBB4. It plays critical roles in embryonic development, wound healing, and pathological processes such as cancer and inflammation. EREG’s overexpression has been linked to tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance in cancers like colorectal, breast, and lung carcinomas, often correlating with poor prognosis.
EREG antibodies are essential tools for studying its biological functions and clinical relevance. These antibodies enable detection of EREG expression and localization via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. In research, they help elucidate EREG’s role in activating downstream signaling pathways (e.g., MAPK, PI3K/AKT) and its crosstalk with tumor microenvironment components. Therapeutically, EREG-neutralizing antibodies are explored for targeting EREG-driven malignancies, while diagnostic applications focus on leveraging EREG as a biomarker for disease monitoring.
Despite progress, challenges remain in understanding tissue-specific EREG regulation and optimizing antibody-based therapies. Ongoing studies aim to clarify its dual roles in promoting both tissue repair and disease progression, highlighting its potential as a multifaceted target in precision medicine.
×