| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
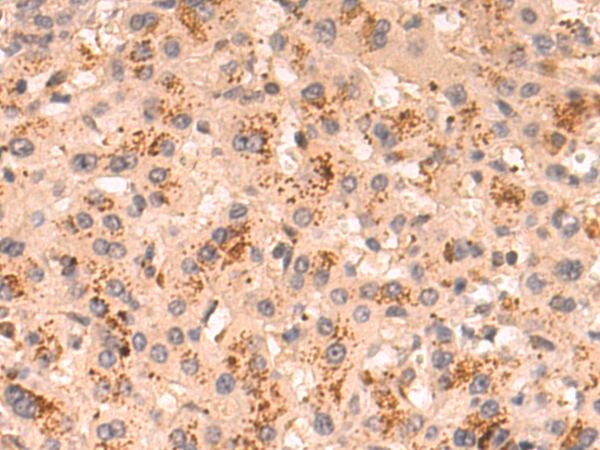
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MHC; HLAC; HLC-C; D6S204; PSORS1; HLA-JY3 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HLA-C |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HLA-C抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要信息:
1. **《HLA Antibody Specificities in Solid Organ Transplantation》**
- 作者:Duquesnoy, R.J.
- 摘要:探讨HLA-C抗体在实体器官移植中的临床意义,指出HLA-C抗体可能导致移植物排斥反应,但相对于HLA-I类其他抗体(如HLA-A/B),其致敏作用较弱,可能与抗原表位暴露程度有关。
2. **《Impact of HLA-C mismatch on outcomes after unrelated donor hematopoietic cell transplantation》**
- 作者:Susaeta, F. et al.
- 摘要:通过回顾性分析造血干细胞移植病例,发现供受体HLA-C不匹配与移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)风险增加相关,提示HLA-C抗体可能在免疫识别中起关键作用。
3. **《HLA-C: A New Frontier in Immune Regulation and Disease Susceptibility》**
- 作者:Trowsdale, J. & Knight, J.C.
- 摘要:综述HLA-C分子的免疫调控功能,强调其与自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞)表面KIR受体互动的特殊性,并讨论HLA-C抗体在自身免疫疾病和病毒感染中的潜在病理机制。
4. **《HLA-C antibodies in pregnancy: A systematic review》**
- 作者:Koehl, U. et al.
- 摘要:分析妊娠期母体HLA-C抗体的产生及其对胎儿发育的影响,提出HLA-C不匹配可能通过抗体介导的免疫反应导致复发性流产或先兆子痫等妊娠并发症。
注:以上文献名为概括性描述,实际检索时可根据关键词(如“HLA-C antibody transplantation/pregnancy”)在PubMed或Web of Science中查找具体论文。
**Background of HLA-C Antibodies**
Human leukocyte antigen C (HLA-C), a class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecule, plays a critical role in immune regulation by presenting peptides to CD8+ T cells and interacting with natural killer (NK) cell receptors (e.g., KIRs). Unlike HLA-A and HLA-B, HLA-C exhibits lower surface expression but is pivotal in immune tolerance, particularly during pregnancy and transplantation. HLA antibodies, including anti-HLA-C, are typically generated through exposure to non-self HLA molecules via blood transfusion, pregnancy, or prior organ transplants.
HLA-C antibodies are clinically significant in transplant medicine, contributing to graft rejection or failure. Their detection via solid-phase assays (e.g., single-antigen bead assays) aids in assessing donor-specific antibodies (DSAs) and guiding HLA matching. Notably, HLA-C mismatches are less immunogenic than HLA-A/B mismatches, yet anti-HLA-C antibodies still correlate with adverse outcomes in kidney and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Emerging research highlights HLA-C’s dual role in viral immunity (e.g., HIV control) and autoimmune diseases, with certain alleles linked to conditions like psoriasis. Despite its lower expression, HLA-C’s interaction with KIRs modulates NK cell activity, influencing immune surveillance and tolerance. Understanding HLA-C antibody dynamics remains crucial for improving transplant protocols and managing alloimmune responses.
×