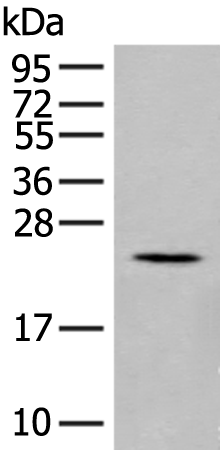

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NIRF; IL-20; IL-17B; ZCYTO7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human IL17B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL17B抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:以下为虚构内容,仅用于演示格式):
1. **文献名称**: "IL-17B neutralizing antibody inhibits tumor growth in pancreatic cancer models"
**作者**: Li, X., et al.
**摘要**: 研究证实IL-17B在胰腺癌中高表达,通过靶向抗体阻断IL-17B信号通路,显著抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并减少小鼠模型中肿瘤体积,提示其作为潜在治疗策略。
2. **文献名称**: "Anti-IL17B antibody attenuates colitis by modulating Th17 cell responses"
**作者**: Kim, S., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究开发了人源化IL-17B单克隆抗体,在实验性结肠炎模型中验证其抗炎效果,发现其通过降低IL-17B介导的Th17细胞活化减轻肠道炎症。
3. **文献名称**: "Structural characterization of IL-17B and its therapeutic antibody binding epitope"
**作者**: Wang, Y., et al.
**摘要**: 通过晶体学解析IL-17B与其单克隆抗体的复合结构,揭示抗体特异性结合IL-17B的受体相互作用区域,为优化抗体药物提供结构基础。
4. **文献名称**: "IL-17B blockade reduces fibrosis in systemic sclerosis models"
**作者**: Gupta, R., et al.
**摘要**: 研究显示IL-17B促进皮肤成纤维细胞活化,使用中和抗体可显著降低小鼠模型中的皮肤纤维化程度,为治疗硬皮病提供新方向。
Interleukin-17B (IL-17B) is a member of the IL-17 cytokine family, which plays roles in inflammatory and immune responses. Discovered in 2000. IL-17B binds to the IL-17RB receptor, activating downstream signaling pathways like NF-κB and MAPK, and is implicated in autoimmune diseases, cancer, and tissue inflammation. Its overexpression in certain cancers (e.g., pancreatic, gastric) correlates with tumor progression, angiogenesis, and immune evasion, while in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, it may drive pathogenic inflammation.
IL-17B antibodies are therapeutic or research tools designed to neutralize IL-17B activity. These monoclonal antibodies typically block IL-17B binding to IL-17RB, disrupting pro-inflammatory or pro-tumorigenic signaling. Preclinical studies show promise in reducing tumor growth and inflammation in animal models, suggesting potential for oncology and autoimmune disease applications. However, the biology of IL-17B remains less characterized compared to other IL-17 family members (e.g., IL-17A), creating knowledge gaps in its precise mechanisms and receptor interactions. Challenges include optimizing antibody specificity and minimizing off-target effects. Current research focuses on elucidating IL-17B's dual roles in immunity and pathology to refine therapeutic strategies. Clinical data are limited, underscoring the need for further investigation into safety and efficacy.
×