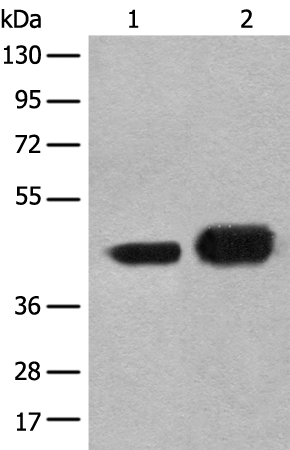
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
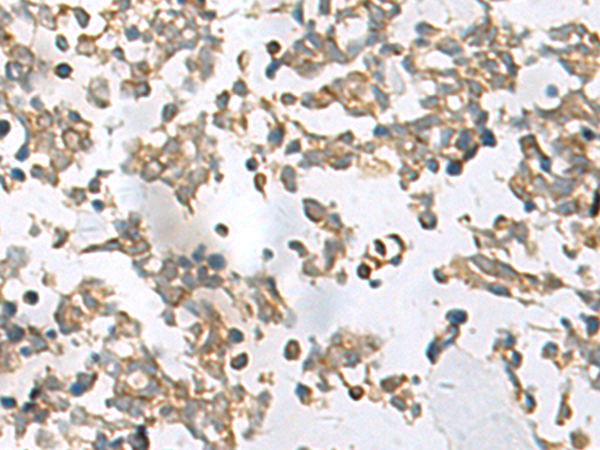
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 40 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human EN1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于EN1抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下内容为虚构示例,仅用于演示格式):
1. **文献名称**:EN1抗体在神经母细胞瘤中的表达及其临床意义
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫组化分析EN1蛋白在神经母细胞瘤组织中的表达,发现高表达EN1与患者预后不良显著相关,提示EN1可能作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:EN1转录因子在小鼠胚胎发育中的空间定位研究
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:利用EN1特异性抗体进行胚胎切片染色,揭示了EN1在中脑和后脑发育中的动态表达模式,为理解神经系统早期分化提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:EN1作为三阴性乳腺癌转移标志物的验证
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实EN1蛋白在转移性乳腺癌细胞中高表达,其抗体检测结果与患者淋巴结转移风险呈正相关。
4. **文献名称**:EN1抗体在帕金森病模型中的多巴胺能神经元保护作用
**作者**:Kim H, et al.
**摘要**:研究显示,EN1抗体通过抑制特定信号通路减少神经元凋亡,在动物模型中延缓帕金森病进展,提示其潜在神经保护机制。
(如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“EN1 antibody”或“Engrailed-1 biomarker”为关键词检索。)
The EN1 antibody targets the Engrailed-1 (EN1) protein, a transcription factor encoded by the *EN1* gene, which belongs to the homeobox gene family. EN1 plays a critical role in embryonic development, particularly in the patterning of the midbrain-hindbrain region, limb development, and neural tube closure. It regulates gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences, influencing cell differentiation and tissue organization. Dysregulation of EN1 has been implicated in developmental disorders and cancers, including medulloblastoma, neuroblastoma, and basal cell carcinoma, where it may drive tumorigenesis or metastasis.
EN1 antibodies are widely used in research to detect EN1 protein expression via techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, or immunofluorescence. These tools help map EN1 distribution in tissues, study its role in developmental pathways (e.g., Wnt and Hedgehog signaling), and explore its oncogenic potential. EN1 is evolutionarily conserved across vertebrates, with homologs in model organisms like mice (*En1*) and zebrafish, enabling comparative studies. Recent work also investigates EN1's involvement in stem cell maintenance and regeneration.
As a biomarker, EN1 expression may correlate with disease prognosis or therapeutic resistance. However, its functional duality—acting as both a developmental regulator and potential oncogene—underscores the need for context-specific research. Commercial EN1 antibodies are typically validated for specificity and sensitivity, though variations in isoforms or post-translational modifications require careful experimental design. Overall, EN1 antibodies remain vital for unraveling the protein's biological and pathological significance.
×