| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
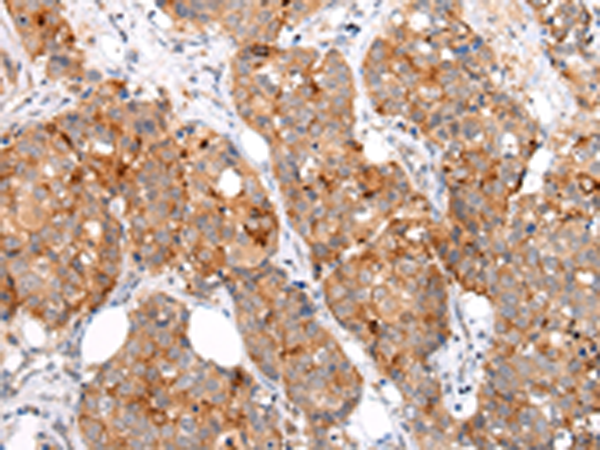
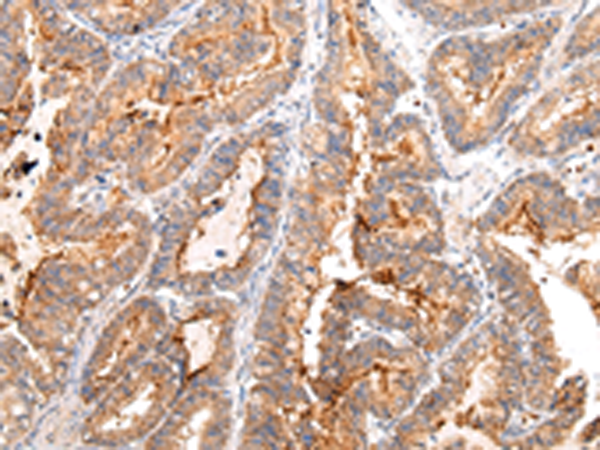
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EMA; MCD; PEM; PUM; KL-6; MAM6; MCKD; PEMT; CD227; H23AG; MCKD1; MUC-1; ADMCKD; ADMCKD1; CA 15-3; MUC-1/X; MUC1/ZD; MUC-1/SEC |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MUC1(CT) |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MUC1(CT)抗体的3篇参考文献概览,涵盖其应用方向和研究背景:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting the cytoplasmic domain of MUC1 with a therapeutic antibody inhibits tumor progression in vitro and in vivo*
**作者**:Li Y. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向MUC1 C末端(CT)结构域的单克隆抗体,验证其在乳腺癌和胰腺癌细胞系中的抗肿瘤活性。实验表明,该抗体通过阻断MUC1与β-catenin的相互作用,抑制Wnt信号通路,从而减少肿瘤细胞增殖和转移。动物模型显示抗体显著抑制肿瘤生长。
---
2. **文献名称**:*MUC1-C-terminal domain-specific antibody targets intracellular oncogenic signaling in triple-negative breast cancer*
**作者**:Raina D. et al.
**摘要**:作者针对MUC1(CT)设计了一种新型抗体,用于靶向三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)中异常激活的MUC1-C端信号通路。研究发现,该抗体选择性结合MUC1的胞内结构域,阻断其与NF-κB和STAT3的相互作用,诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,并增强化疗药物敏感性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*A novel anti-MUC1 antibody-drug conjugate for targeted therapy of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer*
**作者**:Chen W. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用MUC1(CT)特异性抗体偶联化疗药物(ADC),开发了一种针对顺铂耐药卵巢癌的靶向疗法。该抗体通过识别肿瘤细胞中高表达的MUC1胞内结构域,精准递送细胞毒素,在体外和小鼠模型中显著抑制肿瘤进展,且对正常组织毒性较低。
---
**研究方向扩展**:
MUC1(CT)抗体研究多聚焦于癌症靶向治疗,因其在肿瘤细胞中异常高表达且参与致癌信号通路(如Wnt/β-catenin、EGFR)。近年研究趋势包括抗体偶联药物(ADC)、免疫检查点联合疗法,以及针对耐药性肿瘤的精准干预。
The MUC1(CT) antibody specifically targets the C-terminal cytoplasmic tail of the mucin 1 (MUC1) protein, a transmembrane glycoprotein overexpressed in numerous epithelial cancers. MUC1 consists of an extracellular α-subunit with a variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) and a transmembrane β-subunit. Under normal conditions, MUC1 is involved in cell signaling, protection of epithelial surfaces, and immune modulation. However, in cancer, MUC1 is aberrantly overexpressed and undergoes hypoglycosylation, exposing its normally hidden epitopes and promoting oncogenic signaling. The C-terminal region plays a critical role in intracellular signaling by interacting with kinases (e.g., EGFR, Src) and transcription factors (e.g., β-catenin), driving tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance.
MUC1(CT)-specific antibodies are vital tools in cancer research, enabling detection of MUC1 expression and localization via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. These antibodies help elucidate MUC1’s role in tumorigenesis and its interactions with signaling pathways. Therapeutically, targeting MUC1(CT) holds promise for developing monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), or small-molecule inhibitors to disrupt oncogenic signaling. Clinical studies explore MUC1(CT)-targeting agents in cancers such as breast, pancreatic, and ovarian carcinomas. Despite challenges like tumor heterogeneity, MUC1(CT) remains a key focus for precision oncology due to its cancer-specific expression and functional relevance.
×