| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
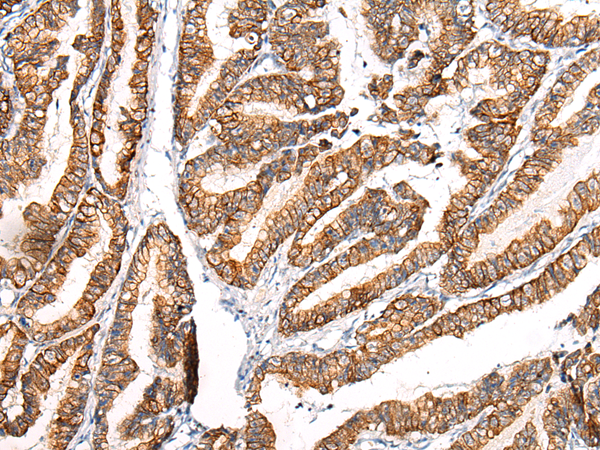
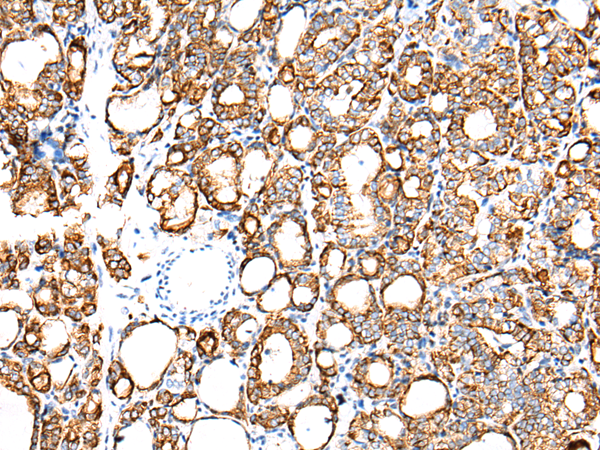
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | K7; CK7; SCL; K2C7 |
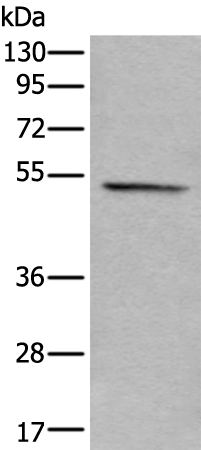
| WB Predicted band size | 51 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human KRT7 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KRT7抗体的3-4篇参考文献的简要总结(文献标题、作者及摘要内容):
---
1. **标题**: *"The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors, and cultured cells"*
**作者**: Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究系统分类了人类细胞角蛋白(包括KRT7),描述了其在正常上皮、肿瘤及培养细胞中的表达模式。KRT7在腺上皮和移行上皮中高表达,而在鳞状上皮中通常缺失,这为后续肿瘤分型提供了重要依据。
2. **标题**: *"Immunohistochemistry for diagnosis of metastatic carcinomas of unknown primary origin"*
**作者**: Chu P, Weiss LM.
**摘要**: 文章讨论了KRT7抗体在鉴别转移性癌原发部位中的应用,指出KRT7常与KRT20联合使用。例如,KRT7+/KRT20-可能提示肺或乳腺来源,而KRT7-/KRT20+则常见于结直肠癌,为临床病理诊断提供参考。
3. **标题**: *"The utility of cytokeratin 7 and 20 immunohistochemistry in the differential diagnosis of primary and metastatic liver carcinomas"*
**作者**: Bass BC, Parwani AV, Ali SZ.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化分析肝肿瘤,发现KRT7在胆管癌中高表达,而在肝细胞癌中多为阴性,表明KRT7抗体有助于区分这两种肝脏原发肿瘤及转移性腺癌。
4. **标题**: *"Cytokeratin 7 and cytokeratin 20 expression in epithelial neoplasms: a survey of 435 cases"*
**作者**: Ramakers CR, van de Molengraft FJ, van Bokhoven A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究统计了435例肿瘤的KRT7/KRT20表达模式,证实KRT7在卵巢癌、肺癌及尿路上皮癌中高表达,但在结直肠癌中多为阴性,强调其在确定肿瘤起源中的诊断价值。
---
以上文献涵盖KRT7在正常组织表达、肿瘤分型及转移癌诊断中的应用,适合作为病理学研究的参考。如需具体期刊信息或页码,可进一步补充。
KRT7 antibody is a diagnostic tool targeting cytokeratin 7 (KRT7), a member of the intermediate filament protein family expressed in epithelial cells. KRT7 plays a structural role in maintaining cellular integrity and mediating cell-cell interactions. As a type II keratin, it pairs with type I keratins (e.g., KRT19) to form heterodimers, contributing to tissue-specific cytoskeletal networks.
KRT7 is predominantly expressed in glandular and transitional epithelia, including tissues like the bile ducts, bladder, and respiratory tract. Its expression pattern makes it a valuable biomarker in pathology, particularly for distinguishing adenocarcinomas from squamous cell carcinomas or identifying tumors of epithelial origin. For example, KRT7 positivity helps differentiate cholangiocarcinoma (KRT7+) from hepatocellular carcinoma (KRT7−) or metastatic adenocarcinomas in the liver.
In diagnostic immunohistochemistry, KRT7 antibodies are often used alongside other markers (e.g., KRT20. TTF-1) to refine tumor classification. It is commonly expressed in carcinomas of the lung, breast, ovary, and urinary tract but absent in many colorectal, prostate, and hepatocellular malignancies. Additionally, KRT7 overexpression has been linked to tumor progression, metastasis, and drug resistance in certain cancers, making it a research focus in oncology.
Despite its utility, interpretation requires context, as KRT7 can occasionally be expressed in non-epithelial tumors (e.g., mesotheliomas) or benign conditions. Overall, the KRT7 antibody remains a cornerstone in diagnostic and research settings for epithelial tumor characterization.
×