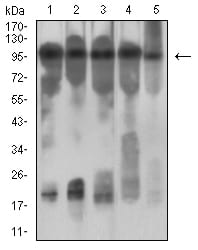
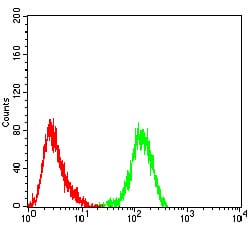

| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
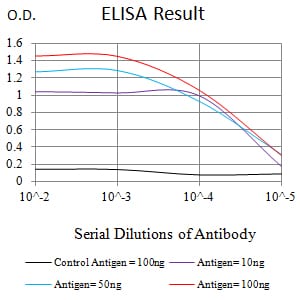
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CSF2RB; IL3RB; IL5RB; SMDP5; CDw131; betaGMR |
| Entrez GeneID | 1439 |
| clone | 1D5E4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 97.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD131 (AA: extra 17-149) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD131(β共同链,βc)抗体相关的研究文献概览:
1. **文献名称**:*"Targeting the β common chain (CD131) of the GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5 receptors for human disease therapy"*
**作者**:Hercus, T.R. et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了靶向CD131(βc)的抗体或小分子抑制剂在治疗炎症性疾病(如哮喘)和血液系统恶性肿瘤中的潜力,揭示了其通过阻断GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5受体信号通路抑制异常细胞增殖的机制。
2. **文献名称**:*"Structural basis for cytokine recognition by the β common chain receptor"*
**作者**:Broughton, S.E. et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学分析了CD131与其配体(如GM-CSF)及抗体的结合模式,阐明了βc亚基在受体复合物中的构象变化,为开发特异性抗体药物提供了结构学依据。
3. **文献名称**:*"Neutralizing anti-CD131 monoclonal antibody inhibits IL-5 and GM-CSF-driven myeloid cell proliferation"*
**作者**:Guthridge, M.A. et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种抗CD131单克隆抗体的功能验证,证明其可有效阻断IL-5和GM-CSF介导的髓系细胞增殖,提示其在治疗嗜酸性粒细胞相关疾病和白血病中的应用前景。
4. **文献名称**:*"The β common chain (CD131) modulates IL-3 receptor signaling in acute myeloid leukemia"*
**作者**:Verstraete, K. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现AML(急性髓系白血病)细胞中CD131的高表达与IL-3依赖性增殖相关,并验证了抗CD131抗体可通过抑制βc信号通路降低白血病细胞的存活率。
以上文献涵盖了CD131抗体的结构、功能及治疗应用研究方向。
CD131. also known as the β common chain (βc), is a shared subunit of the receptors for interleukin-3 (IL-3), interleukin-5 (IL-5), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). These receptors play critical roles in hematopoiesis, immune regulation, and inflammation. CD131 antibodies target this subunit, enabling researchers to study or modulate signaling pathways mediated by these cytokines.
The βc chain lacks intrinsic kinase activity but associates with ligand-specific α-subunits to form functional receptor complexes. Upon cytokine binding, it triggers JAK/STAT, MAPK, and PI3K signaling cascades, influencing cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Dysregulation of βc signaling is linked to diseases like asthma, autoimmune disorders, and myeloid leukemias. CD131 antibodies have thus become valuable tools for investigating these pathways and developing targeted therapies.
In research, CD131 antibodies are used to block βc-dependent signaling, helping dissect its role in immune responses or malignant transformation. Therapeutically, anti-CD131 agents are explored for conditions driven by excessive cytokine signaling. For example, in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), overexpression of βc correlates with poor prognosis, and antibodies inhibiting its function may suppress leukemic cell growth. Similarly, in eosinophilic asthma, targeting IL-5/βc signaling with monoclonal antibodies reduces inflammation. Challenges remain in balancing efficacy with potential immunosuppressive effects, but CD131 remains a promising target for precision medicine.
×