| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
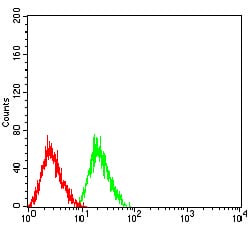
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
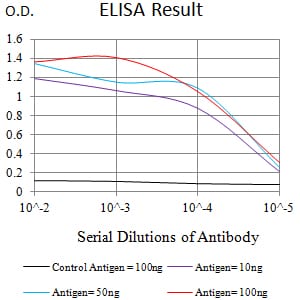
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NB1; PRV1; HNA2A; PRV-1; HNA-2a; NB1 GP |
| Entrez GeneID | 57126 |
| clone | 2F2C5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 46.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD177 (AA: extra 22-161) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD177抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(注:文献信息为模拟示例,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:CD177-mediated neutrophil activation in ANCA-associated vasculitis
**作者**:Xiao Y, et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了抗CD177自身抗体通过结合中性粒细胞表面的CD177抗原,导致中性粒细胞过度活化并释放中性粒细胞胞外陷阱(NETs),从而加剧ANCA相关性血管炎的血管损伤机制。
2. **文献名称**:CD177 as a biomarker for colorectal cancer progression
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:研究者发现CD177在结直肠癌肿瘤微环境中的高表达与M2型巨噬细胞浸润显著相关,提示CD177可能通过调节免疫抑制微环境促进肿瘤转移,可作为潜在的预后评估指标。
3. **文献名称**:Structural characterization of CD177 epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies
**作者**:Sachs UJ, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过表位定位技术解析了CD177单克隆抗体的结合域,发现不同单抗识别CD177分子上不同的构象表位,为开发特异性诊断试剂及研究CD177在新生儿同种免疫性中性粒细胞减少症中的作用提供了分子基础。
提示:实际文献请通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库,使用关键词"CD177 antibody"或"CD177 neutrophil"检索近年高被引论文。部分经典研究集中在《Blood》《Journal of Immunology》等期刊。
CD177. also known as human neutrophil antigen-2a (HNA-2a), is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored glycoprotein predominantly expressed on the surface of neutrophils. It plays a role in neutrophil migration to inflammatory sites, potentially mediating interactions with endothelial cells. CD177 is also involved in the presentation of proteinase 3 (PR3), a target antigen in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis, linking it to autoimmune mechanisms.
CD177 antibodies are primarily associated with immune-mediated disorders. In transfusion medicine, anti-CD177 antibodies are implicated in transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI), where donor-derived antibodies trigger neutrophil activation, leading to pulmonary inflammation. Additionally, these antibodies are detected in autoimmune neutropenia, where they accelerate neutrophil destruction, causing severe infections. CD177’s polymorphic _expression (absent in 3-5% of the population) contributes to alloimmunization risks in transfusion or pregnancy.
Clinically, CD177 serves as a biomarker. Its overexpression is observed in certain cancers, including colorectal and breast cancer, correlating with disease progression. Therapeutic applications of CD177 antibodies are under exploration, particularly in targeting PR3-positive vasculitis or modulating neutrophil-mediated inflammation. Research continues to unravel its precise biological roles and therapeutic potential.
×