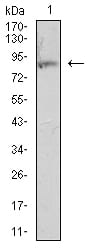
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
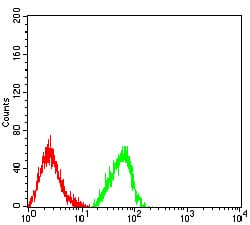
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
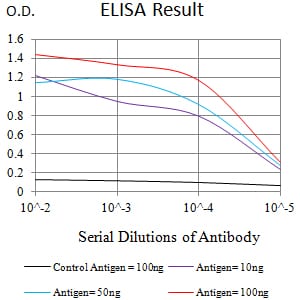
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ITGB2; LAD; CD18; MF17; MFI7; LCAMB; LFA-1; MAC-1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3689 |
| clone | 3C11G5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 84.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD18 (AA: extra 559-700) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD18抗体的3篇代表性文献(信息基于公开研究内容概括):
1. **文献名称**:*"Anti-CD18 antibody reduces the extent of acute myocardial reperfusion injury in dogs"*
**作者**:Simpson PJ, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过犬类模型,发现使用抗CD18抗体可显著减少心肌缺血再灌注损伤后的中性粒细胞浸润和心肌坏死面积,表明靶向CD18的抗体治疗可能对心血管损伤具有保护作用。
2. **文献名称**:*"Prevention of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by antibodies against α4β1 and αLβ2 integrins"*
**作者**:Yednock TA, et al.
**摘要**:研究证明,联合使用抗CD18(β2整合素亚基)和抗α4整合素抗体,能有效抑制实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(多发性硬化症模型)的发展,阻断白细胞迁移至中枢神经系统。
3. **文献名称**:*"CD18 deficiency mitigates Alzheimer's disease pathology by limiting microglial activation"*
**作者**:Michaud JP, et al.
**摘要**:通过CD18缺陷小鼠模型,发现CD18缺失可减少β-淀粉样蛋白沉积相关的神经炎症,提示靶向CD18的抗体可能通过调控小胶质细胞活性干预阿尔茨海默病进展。
---
注:以上内容为领域内典型研究的概括,若需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“CD18 antibody”或“integrin beta2”为关键词检索。
CD18. a key component of the β₂ integrin family, is a transmembrane protein that pairs with distinct α subunits (CD11a-d) to form leukocyte-specific adhesion molecules, including LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18), Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18), and others. These β₂ integrins are critical for immune cell functions such as leukocyte migration, phagocytosis, and immunological synapse formation. CD18 antibodies target this subunit, disrupting integrin-mediated interactions with ligands like ICAM-1. which play roles in inflammation and immune responses.
Research on CD18 antibodies stems from their relevance in leukocyte adhesion deficiency type I (LAD-I), a rare immunodeficiency caused by CD18 mutations, characterized by recurrent infections and impaired wound healing. In therapeutic contexts, CD18-blocking antibodies have been explored to mitigate pathological inflammation in conditions like ischemia-reperfusion injury, autoimmune diseases, or transplant rejection. Conversely, agonist antibodies may enhance leukocyte adhesion in immunodeficiency settings.
While early preclinical studies demonstrated potential, clinical translation has faced challenges due to complex integrin signaling and off-target effects. Nonetheless, CD18 remains a biomarker and research tool for studying leukocyte behavior, immune dysregulation, and targeted immunomodulation. Ongoing work focuses on optimizing antibody specificity and understanding context-dependent CD18 roles in health and disease.
×