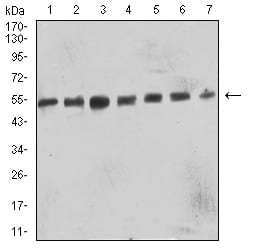
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
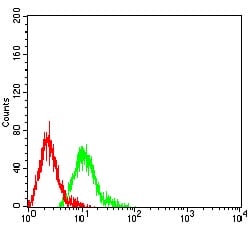
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
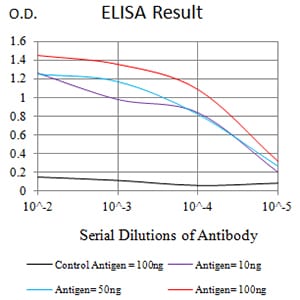
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B3GAT1; NK1; HNK1; LEU7; NK-1; GLCATP; GLCUATP |
| Entrez GeneID | 27087 |
| clone | 3F6D6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD57 (AA: 35-191) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD57抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概览:
---
1. **文献名称**: *CD57 identifies a subset of polyfunctional CD8+ T cells in chronic viral infections*
**作者**: Buggert M, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过CD57抗体标记发现,在慢性HIV和HCV感染中,CD8+ T细胞中高表达CD57的亚群表现出较低的增殖能力和细胞毒性,但具有更强的多细胞因子分泌能力,提示CD57可能作为T细胞功能耗竭的标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**: *CD57+ NK cells associate with exacerbation of symptoms in chronic Lyme disease*
**作者**: Marques A, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究发现,慢性莱姆病患者外周血中CD57+自然杀伤细胞(NK细胞)数量显著减少,且与症状严重程度呈负相关,提示CD57抗体可作为评估免疫功能障碍的生物标志物。
---
3. **文献名称**: *CD57 expression in glioblastoma correlates with tumor progression and survival*
**作者**: Hussain SF, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用CD57抗体分析胶质母细胞瘤组织,发现CD57高表达的肿瘤微环境中调节性T细胞(Treg)浸润增加,且与患者总生存期缩短相关,表明CD57可能参与肿瘤免疫抑制机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核实具体信息。
CD57. also known as HNK-1 or Leu-7. is a cell surface glycoprotein originally identified as a marker for natural killer (NK) cells and a subset of T lymphocytes. It recognizes a carbohydrate epitope (3-O-sulfoglucuronic acid) linked to glycolipids or glycoproteins, commonly expressed on neural cells (e.g., Schwann cells, neurons) and cytotoxic lymphocytes. CD57 antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to identify terminally differentiated effector T cells, senescent T cells, and NK cells, as well as to study neural development and regeneration.
In immunology, CD57⁺ T cells are associated with replicative senescence, chronic viral infections (e.g., HIV, CMV), and age-related immune dysfunction. Clinically, CD57 antibodies aid in diagnosing certain lymphoproliferative disorders (e.g., aggressive NK-cell leukemia) and neuroendocrine tumors. In neurobiology, they help assess nerve injury and demyelinating diseases. However, CD57 expression varies across tissues and pathologies, requiring careful interpretation. Its role in immune exhaustion and tissue-specific functions remains an active research area, highlighting its dual significance in immunity and neural biology.
×