| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
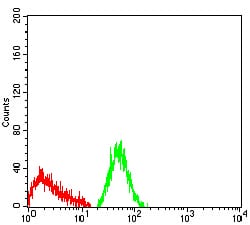
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
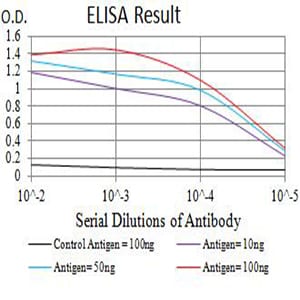
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CEACAM1; BGP; BGP1; BGPI |
| Entrez GeneID | 634 |
| clone | 4F3B2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD66A (AA: extra 65-201) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD66A(CEACAM1)抗体的3篇参考文献,按作者和摘要内容概括列举:
1. **"CEACAM1: A multifunctional human cell adhesion molecule"**
- **作者**: Beauchemin, N., et al.
- **摘要**: 该文献综述了CEACAM1(CD66A)作为细胞黏附分子的功能,包括其在结肠癌中的表达调控及在肿瘤进展中的作用。研究利用特异性抗体揭示了其在细胞间信号传导和上皮组织分化中的关键角色。
2. **"CD66 antigens mediate interactions between human neutrophils and endothelial cells"**
- **作者**: Skubitz, K.M., et al.
- **摘要**: 本文通过抗CD66A抗体实验,证实CD66家族(尤其是CEACAM1)在中性粒细胞与血管内皮细胞黏附过程中的作用,为炎症反应的分子机制提供了新见解。
3. **"CEACAM1: A novel target for cancer immunotherapy"**
- **作者**: Gray-Owen, S.D., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究使用抗CD66A抗体探讨了CEACAM1在肿瘤免疫逃逸中的功能,提出其作为免疫检查点分子的潜力,并评估了靶向抗体在癌症治疗中的应用前景。
如需具体文献来源或补充更多内容,可进一步说明。
CD66a antibody targets the CD66a antigen, also known as CEACAM1 (Carcinoembryonic Antigen-Related Cell Adhesion Molecule 1), a member of the CEACAM family of glycoproteins. CEACAM1 is a transmembrane receptor with roles in cell adhesion, signaling, and immune regulation. It contains immunoglobulin-like domains and exhibits multiple isoforms due to alternative splicing, influencing its function in different tissues. CD66a is expressed on epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and immune cells (e.g., T cells, neutrophils), where it modulates intercellular interactions, immune responses, and pathogen recognition.
In cancer biology, CEACAM1 has dual roles, acting as a tumor suppressor or promoter depending on context. It is often dysregulated in malignancies (e.g., colorectal, lung cancers) and may contribute to immune evasion. CD66a antibodies are used in research to study CEACAM1's involvement in tumor progression, immune checkpoint regulation, and microbial pathogenesis (e.g., Neisseria species exploit CEACAM1 for host cell adhesion). These antibodies are also tools in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional assays to explore CEACAM1's interactions with ligands or its role in signaling pathways. Therapeutic applications, such as blocking CEACAM1 to enhance anti-tumor immunity, remain under investigation.
×