| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
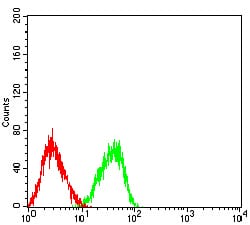
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
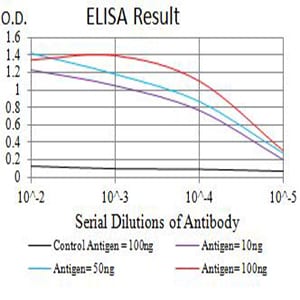
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LY9B; hCD84; mCD84; SLAMF5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 8832 |
| clone | 5D12H10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD84 (AA: extra 22-225) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD84抗体的3篇文献摘要示例:
---
1. **文献名称**:*CD84 regulates T cell responses in autoimmune inflammation*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究探讨CD84在自身免疫性炎症中的调节作用,发现CD84抗体通过抑制T细胞活化和细胞因子分泌,减轻小鼠模型中的炎症反应。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD84 in B-cell malignancies with a novel monoclonal antibody*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型抗CD84单克隆抗体的开发,显示其在体外和体内实验中能特异性结合B细胞恶性肿瘤细胞,并诱导凋亡,提示其作为淋巴瘤治疗的潜在药物。
---
3. **文献名称**:*CD84 mediates platelet adhesion and thrombus formation via homophilic interactions*
**作者**:Chen H, et al.
**摘要**:揭示CD84通过同源相互作用促进血小板黏附和血栓形成,阻断CD84抗体可显著减少实验性血栓模型中的血栓大小,为抗血栓治疗提供新靶点。
---
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。如需具体文献,请提供更详细的研究方向或关键词。
CD84 is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family, which plays a role in immune regulation. Encoded by the *CD84* gene in humans, it consists of an extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domain, a transmembrane region, and a cytoplasmic tail containing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motifs (ITSMs). CD84 is expressed on various immune cells, including B cells, T cells, dendritic cells, and platelets, and functions as a homophilic adhesion molecule, binding to CD84 on adjacent cells to mediate cell-cell interactions.
Studies suggest CD84 participates in modulating immune cell activation, survival, and signal transduction. In platelets, it contributes to aggregation and thrombus formation by reinforcing integrin-mediated signaling. Its role in B-cell malignancies, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), has drawn attention, as elevated CD84 expression correlates with disease progression and drug resistance. CD84 antibodies—either monoclonal or polyclonal—are widely used in research to block its signaling, study receptor-ligand interactions, or detect its expression via flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry.
Therapeutic potential is being explored, particularly in targeting CD84 in autoimmune disorders or hematologic cancers. However, its dual roles in immune activation and inhibition, depending on context, complicate clinical applications. Ongoing research aims to unravel its precise mechanisms and evaluate CD84-targeting antibodies as biomarkers or therapeutic agents.
×