| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
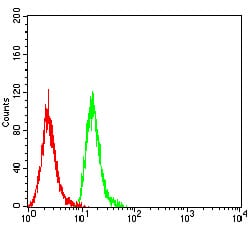
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
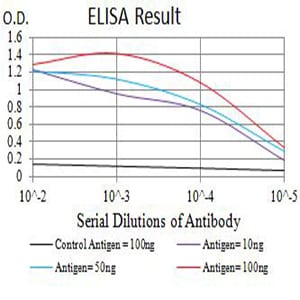
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LY9B; hCD84; mCD84; SLAMF5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 8832 |
| clone | 5B9E10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD84 (AA: extra 22-225) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD84抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **"CD84 regulates platelet activation and thrombosis"**
- **作者**: Hofherr et al.
- **摘要**: 研究CD84在血小板活化和血栓形成中的作用,发现CD84抗体可抑制血小板聚集及信号传导,提示其作为抗血栓治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **"CD84 modulates B cell immune response through interaction with SLAMF receptors"**
- **作者**: Romero et al.
- **摘要**: 揭示CD84通过SLAM家族受体调控B细胞活化和抗体分泌,使用单克隆抗体阻断CD84可减少自身免疫模型中的炎症反应。
3. **"Therapeutic targeting of CD84 in hematological malignancies"**
- **作者**: Chen et al.
- **摘要**: 探索CD84在白血病和淋巴瘤中的高表达,通过抗体靶向CD84可诱导癌细胞凋亡并增强化疗敏感性,为血液肿瘤治疗提供新策略。
CD84 is a cell surface glycoprotein belonging to the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM) family, which plays a role in immune regulation and cell-cell communication. It is encoded by the *CD84* gene and expressed primarily on immune cells, including B cells, T cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, and platelets. Structurally, CD84 contains extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig)-like domains, a transmembrane region, and cytoplasmic tyrosine-based signaling motifs that recruit adaptor proteins like SAP (SLAM-associated protein). Its interactions, often homophilic (binding to CD84 on adjacent cells), modulate immune responses such as cell activation, adhesion, and cytokine production.
CD84 antibodies are tools used to study this protein's expression, function, and involvement in diseases. Research suggests CD84 is implicated in autoimmune disorders, hematologic malignancies, and inflammatory conditions. For example, elevated CD84 expression has been observed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and lupus, making it a potential biomarker or therapeutic target. Antibodies targeting CD84 have been utilized in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and functional assays to explore its role in immune signaling pathways or tumor microenvironments. Recent studies also investigate CD84 antibodies in preclinical models for blocking pathogenic interactions or delivering cytotoxic agents in cancer therapy. However, its precise mechanisms and therapeutic potential remain under active investigation, highlighting the need for further characterization of CD84-specific antibody applications.
×