| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
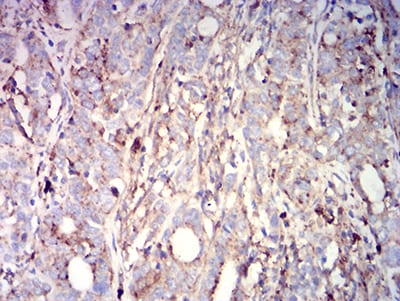
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
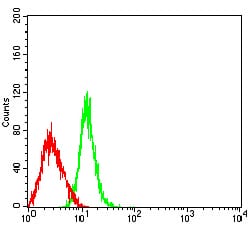
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
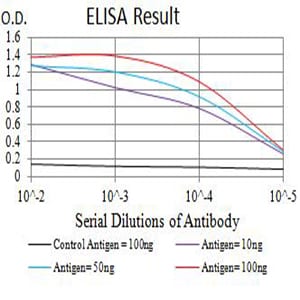
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MLA1; ME491; LAMP-3; OMA81H; TSPAN30 |
| Entrez GeneID | 967 |
| clone | 1H3E3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD63 (AA: extra 103-203) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD63抗体的代表性文献,按研究主题分类:
1. **文献名称**:*Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids*
**作者**:Théry C, et al.
**摘要**:该文献系统总结了外泌体分离和鉴定的标准化方法,提出CD63抗体作为外泌体表面标志物的关键工具,用于免疫捕获和流式检测。
2. **文献名称**:*Proteomic analysis of dendritic cell-derived exosomes: A secreted subcellular compartment distinct from apoptotic vesicles*
**作者**:Van Niel G, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用CD63抗体结合质谱技术,揭示了树突状细胞来源外泌体的蛋白质组成,证明CD63在胞内运输和分泌过程中的特异性定位。
3. **文献名称**:*Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis*
**作者**:Hoshino A, et al.
**摘要**:通过CD63抗体富集肿瘤外泌体,发现外泌体表面整合素可作为转移器官倾向性的生物标志物,CD63阳性外泌体在癌症转移中起关键调控作用。
4. **文献名称**:*Selective enrichment of tetraspan proteins on the internal vesicles of multivesicular endosomes and on exosomes secreted by human B-lymphocytes*
**作者**:Escola JM, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用CD63抗体验证四跨膜蛋白(如CD63)在多泡内体和外泌体中的特异性分布,为外泌体生物发生机制提供实验依据。
以上文献均以CD63抗体为核心实验工具,涉及外泌体分离、功能研究和疾病机制探索。如需具体期刊和年份,可进一步补充检索。
CD63 antibody targets the CD63 protein, a member of the tetraspanin (transmembrane 4 superfamily, TM4SF) family. CD63 is a cell surface glycoprotein with four transmembrane domains, primarily localized in late endosomes, lysosomes, and lysosome-related organelles such as platelet dense granules and melanosomes. It plays roles in cell adhesion, signal transduction, and intracellular trafficking, and is a recognized marker for exosomes and extracellular vesicles (EVs). CD63 interacts with integrins, growth factor receptors, and other tetraspanins to modulate cellular processes like immune response, cancer metastasis, and pathogen entry.
CD63 antibodies are widely used in research to study exosome biogenesis, vesicle trafficking, and cellular communication. They are employed in techniques like flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, Western blotting, and ELISA to detect CD63 expression, quantify exosomes, or isolate EVs. In clinical contexts, altered CD63 levels are linked to cancers, immune disorders, and lysosomal storage diseases. For example, CD63 overexpression in tumors may correlate with invasion potential, while its deficiency is associated with Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Researchers also utilize CD63 antibodies to explore therapeutic exosome engineering or EV-based diagnostics. As exosome research expands, CD63 remains a critical tool for understanding EV biology and their pathophysiological roles.
×