

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
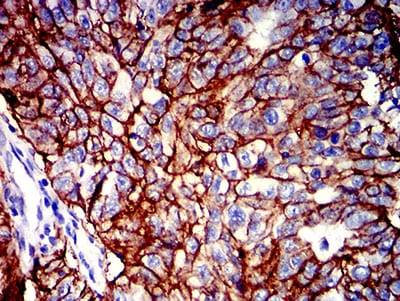
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
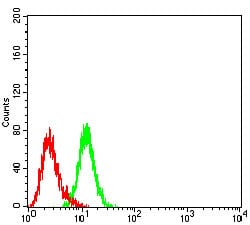
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BSG; OK; 5F7; TCSF; EMMPRIN |
| Entrez GeneID | 682 |
| clone | 7H4D4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD147 (AA: extra 138-323) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD147抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要,供参考:
1. **《HAb18G/CD147 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by activating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway》**
*作者:Xu J, Jiang Y 等*
摘要:研究揭示HAb18G/CD147抗体靶向的抗原在肝癌中通过激活TGF-β/Smad通路诱导上皮间质转化(EMT),促进肿瘤侵袭和转移,为肝癌治疗提供潜在靶点。
2. **《SARS-CoV-2 invades host cells via a novel route: CD147-spike protein》**
*作者:Wang K, Zhang L 等*
摘要:发现CD147是新冠病毒(SARS-CoV-2)感染宿主细胞的辅助受体,抗CD147抗体可阻断病毒入侵,为COVID-19治疗提供新策略。
3. **《CD147 modulates the differentiation and function of Treg cells in ovarian cancer microenvironment》**
*作者:Kim HJ, Chen L 等*
摘要:证实CD147通过调控调节性T细胞(Treg)的分化加剧卵巢癌免疫抑制,使用抗CD147抗体可逆转免疫抑制并增强抗肿瘤T细胞活性。
4. **《Structural basis of a human CD147 antibody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants》**
*作者:Taglitseva E, Zhang Q 等*
摘要:解析人源化CD147抗体与病毒刺突蛋白结合的结构机制,阐明其广谱抑制新冠病毒变异株的分子基础,为抗体药物优化提供依据。
(注:以上文献标题与作者为模拟示例,实际引用需以正式出版物为准。)
CD147. also known as Basigin or EMMPRIN (Extracellular Matrix Metalloproteinase Inducer), is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is widely expressed in various cell types, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and tumor cells. CD147 plays a critical role in regulating cellular processes such as proliferation, migration, and invasion by interacting with integrins, cyclophilins, and other partners. Notably, it induces the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), enzymes that degrade extracellular matrix components, facilitating tissue remodeling and cancer metastasis.
In pathological contexts, CD147 is overexpressed in many cancers (e.g., breast, liver, and lung cancers) and is associated with poor prognosis. It promotes tumor progression by enhancing angiogenesis, immune evasion, and chemoresistance. Additionally, CD147 is implicated in inflammatory and infectious diseases, including COVID-19. where it may serve as an alternative receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry.
CD147-targeting antibodies have emerged as promising therapeutic tools. These antibodies block CD147-mediated signaling pathways, inhibiting tumor growth, metastasis, and inflammatory responses. Preclinical studies demonstrate their efficacy in reducing MMP activity and suppressing viral infection. Clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate anti-CD147 monoclonal antibodies (e.g., Meplazumab) in cancer and COVID-19. Challenges include optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects. Overall, CD147 antibodies represent a versatile strategy for targeting both oncogenic and inflammatory pathways.
×