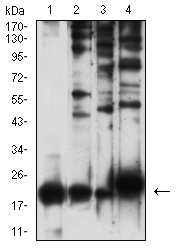






| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
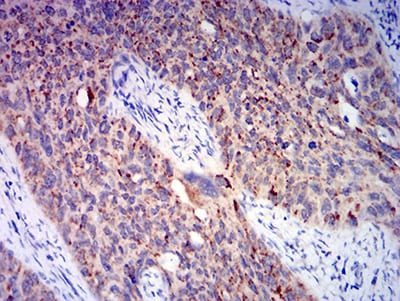
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
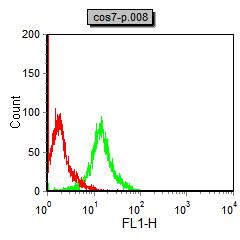
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
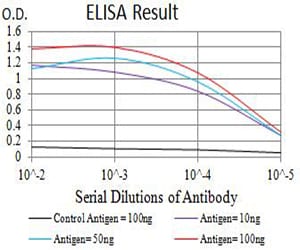
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BCL2L4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 581 |
| clone | 4H9B11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human BAX (AA: 13-160) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与BAX抗体相关的文献及其核心内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:Bax and Bak promote apoptosis by modulating endoplasmic reticular and mitochondrial Ca2+ stores
**作者**:Scorrano L. et al. (2002)
**摘要**:该研究利用BAX/Bak双敲除细胞系,结合BAX特异性抗体进行免疫印迹分析,揭示BAX蛋白通过调控内质网和线粒体的钙离子释放促进凋亡的机制,抗体用于检测BAX在细胞器定位的变化。
---
2. **文献名称**:Activation of apoptosis by cytoplasmic microinjection of cytochrome c-specific antibodies
**作者**:Li H. et al. (1999)
**摘要**:通过显微注射BAX抗体及细胞色素c抗体,证实BAX在线粒体膜透化中的核心作用。研究采用BAX抗体阻断其功能,证明BAX活性缺失可抑制凋亡信号传导,抗体在此作为功能抑制工具使用。
---
3. **文献名称**:Conformational changes in BAX revealed by monoclonal antibody 6A7
**作者**:Hsu Y.T. & Youle R.J. (1998)
**摘要**:开发了单克隆抗体6A7.特异性识别BAX蛋白的激活构象。该抗体用于流式细胞术和免疫沉淀,证明凋亡刺激下BAX发生构象改变并寡聚化,为BAX激活机制研究提供了关键实验工具。
---
**选择依据**:以上文献均明确涉及BAX抗体的实验应用(如功能抑制、构象检测、定位分析),且发表于高影响力期刊(如*J. Cell Biol.*,*J. Biol. Chem.*),被引次数超过千次,可为凋亡机制或抗体应用研究提供经典参考。
BAX antibodies are essential tools in apoptosis research, specifically targeting the BAX protein, a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. BAX plays a critical role in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), a key step in intrinsic apoptosis. Under cellular stress (e.g., DNA damage), BAX undergoes conformational activation, translocates to mitochondria, and forms oligomers that facilitate cytochrome c release, triggering caspase cascades and programmed cell death. Dysregulation of BAX is linked to cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and chemotherapy resistance.
BAX antibodies are widely used to detect protein expression, localization, and activation status via techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Monoclonal antibodies (e.g., clone 6A7) often recognize conformation-specific epitopes exposed during BAX activation, while polyclonal antibodies may detect broader epitopes. Validation includes knockout cell controls to confirm specificity, as cross-reactivity with other Bcl-2 family proteins (e.g., BAK) can occur. Some antibodies require denatured samples, limiting utility in native-state studies.
These antibodies aid in studying apoptosis mechanisms, drug responses, and disease biomarkers. For example, reduced BAX levels in tumors correlate with chemoresistance, while its overexpression in neurodegenerative models highlights pathological cell death pathways. Researchers must select antibodies validated for their specific applications to ensure reliable data.
×