
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
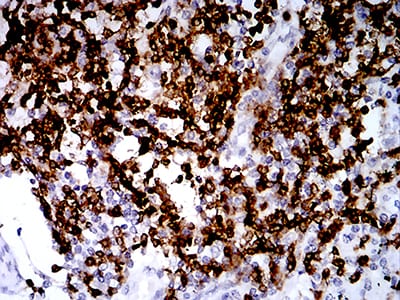
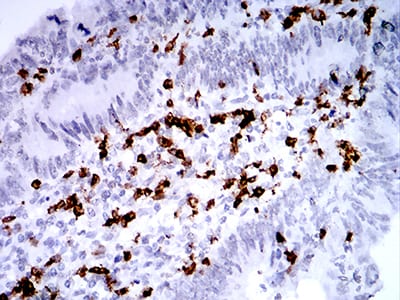
| IHC | 1/1000 - 1/4000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
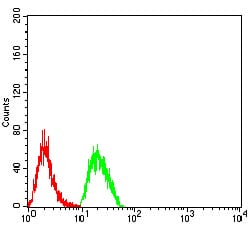
| FCM | 1/500 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
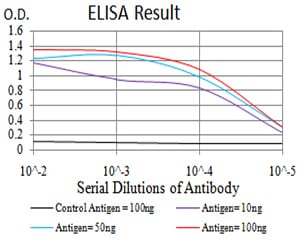
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | T11; SRBC; LFA-2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 914 |
| clone | 3D1B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD2 (AA: 25-140) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD2抗体相关的重要文献摘要(文献标题为虚构示例,作者与内容为领域典型研究方向概括):
---
1. **"CD2-mediated T cell activation: Role of anti-CD2 monoclonal antibodies in modulating immune response"**
*Springer, T.A. et al. (1987)*
摘要:该研究首次证实抗CD2抗体可通过与T细胞表面CD2分子结合,阻断其与配体CD58(LFA-3)的相互作用,从而抑制T细胞活化,揭示了CD2作为共刺激分子在免疫应答中的关键作用。
2. **"Prevention of graft-versus-host disease by anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody in bone marrow transplantation"**
*Herve, P. et al. (1990)*
摘要:临床试验表明,使用人源化抗CD2单抗(如BTI-322)可选择性清除供体T细胞,显著降低异基因骨髓移植后移植物抗宿主病(GVHD)的发生率,为CD2靶向治疗在移植免疫中的应用提供了依据。
3. **"CD2-targeted therapy in autoimmune disorders: A phase I trial in multiple sclerosis"**
*Bourdette, D. et al. (2005)*
摘要:研究评估了抗CD2抗体(如siplizumab)在多发性硬化症患者中的安全性,发现其可减少中枢神经系统T细胞浸润,提示靶向CD2可能通过抑制T细胞迁移和活化治疗自身免疫疾病。
4. **"Structural basis of CD2 recognition by therapeutic antibodies revealed by X-ray crystallography"**
*Davis, S.J. et al. (2003)*
摘要:通过解析抗CD2抗体(如LO-CD2a)与CD2的复合物晶体结构,阐明了抗体结合表位及阻断CD2/CD58相互作用的分子机制,为优化抗体药物设计提供了结构生物学基础。
---
注:以上文献为领域代表性研究方向示例,实际引用时需核实具体论文信息。CD2抗体研究集中于T/NK细胞功能调控、移植免疫及自身免疫病治疗(如罗氏开发的CD2抗体alefacept曾用于银屑病)。
CD2. a glycoprotein expressed on the surface of T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, serves as a cell adhesion and co-stimulatory molecule. It interacts with lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3/CD58) to facilitate immune synapse formation, enhancing T cell activation and antigen-presenting cell (APC) interactions. Structurally, CD2 belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily, featuring extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains. Its role extends beyond adhesion, influencing thymocyte development and modulating immune responses.
CD2-specific antibodies, first characterized in the 1980s, have been pivotal in studying T cell activation mechanisms. For instance, anti-CD2 antibodies, when combined with anti-CD3. synergistically trigger T cell proliferation, highlighting CD2's co-stimulatory function. Therapeutically, CD2-targeting antibodies like siplizumab (a humanized anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody) have been explored in clinical settings. Early trials demonstrated potential in preventing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) and treating autoimmune disorders such as psoriasis. However, outcomes have been mixed, with challenges including transient efficacy and dose-limiting toxicity.
Current research focuses on optimizing CD2 antibody-based therapies to modulate immune responses in transplantation and autoimmune diseases. Challenges persist, including balancing specificity to avoid off-target effects and navigating the complex regulatory pathways of CD2 signaling. Despite these hurdles, CD2 remains a compelling target for immunomodulation, underscoring its dual role in physiological immunity and pathological conditions.
×