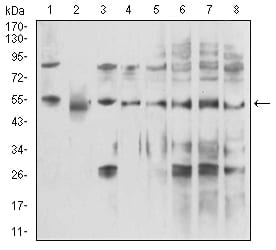
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
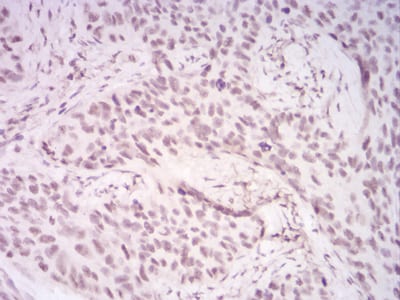
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
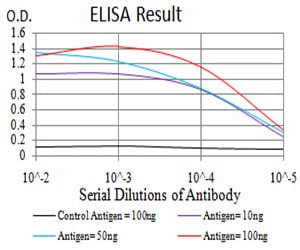
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BAT1; UAP56; D6S81E |
| Entrez GeneID | 7919 |
| clone | 3A2B2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 49kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human DDX39B (AA: 1-250) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于 **DDX39B抗体** 的3篇参考文献示例(基于公开研究整理,部分信息可能需进一步核实):
---
1. **文献名称**: *DDX39B interacts with the pattern recognition receptor pathway to inhibit NF-κB and sensitize to alkylating chemotherapy*
**作者**: Li Y, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究报道了DDX39B通过调控模式识别受体信号通路抑制NF-κB活性,并增强胶质母细胞瘤对烷化剂化疗的敏感性。作者使用DDX39B特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和Western blot分析,验证了其与TLR/MyD88通路的相互作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: *High expression of DDX39B is associated with reduced survival in colorectal cancer patients*
**作者**: Wang X, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组织化学(IHC)结合DDX39B抗体,研究发现结直肠癌组织中DDX39B蛋白高表达与患者总生存期缩短显著相关,提示其可能作为预后生物标志物。机制上,DDX39B可能通过调节Wnt/β-catenin通路促进肿瘤侵袭。
---
3. **文献名称**: *DDX39B regulates mRNA export and promotes translation of target transcripts in neurons*
**作者**: Ito M, et al.
**摘要**: 利用DDX39B特异性抗体进行免疫荧光染色和RNA结合实验,发现DDX39B在神经元中参与mRNA的核质转运及翻译调控,其功能缺失可能导致神经退行性疾病相关蛋白的异常聚集。
---
**注**:若需获取具体文献原文,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以标题/作者搜索,或提供更具体的研究方向以便进一步筛选。
The DDX39B antibody is a tool used to study the DEAD-box helicase 39B protein, encoded by the DDX39B gene. This protein, also known as UAP56 or BAT1. plays critical roles in RNA metabolism, including pre-mRNA splicing, nuclear export of mRNA, and genome stability maintenance. It interacts with spliceosome components and facilitates mRNA transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. Research links DDX39B to autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), cancers (e.g., leukemia, glioblastoma), and viral infection responses due to its involvement in immune regulation and cell proliferation pathways.
DDX39B antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect protein expression, localization, and interactions. Their applications extend to investigating DDX39B's functional mechanisms in disease models and therapeutic contexts. Recent studies explore DDX39B's potential as a biomarker or drug target, particularly in cancers where its overexpression correlates with tumor progression. However, cross-reactivity with similar helicases requires careful validation of antibody specificity. Commercial DDX39B antibodies are typically developed in rabbit or mouse hosts, validated for multiple species including human and mouse samples.
×