| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
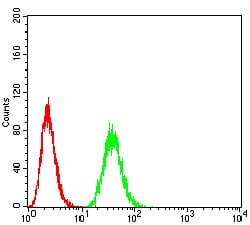
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
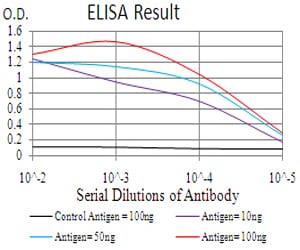
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DYT6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 55145 |
| clone | 2F1B4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 24.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human THAP1 (AA: 1-213) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于THAP1抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*THAP1 mutations cause dystonia with combined respiratory and vocal cord dysfunction*
**作者**:Campagne S, et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了THAP1基因突变与DYT6型肌张力障碍的关联,并利用特异性抗体检测患者细胞中THAP1蛋白表达异常,发现突变导致其转录抑制功能受损。
2. **文献名称**:*The THAP-zinc finger protein THAP1 regulates endothelial cell proliferation through modulation of pRB/E2F cell cycle target genes*
**作者**:Cayrol C, et al.
**摘要**:通过THAP1抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和Western blot实验,发现THAP1通过结合靶基因启动子调控细胞周期,并参与血管内皮细胞增殖。
3. **文献名称**:*Effects of DYT6/THAP1 mutations on protein stability and dimer formation*
**作者**:Lohmann K, et al.
**摘要**:利用THAP1抗体分析突变体蛋白的稳定性及二聚化能力,发现部分突变(如F81L)导致蛋白降解加速,影响其与DNA或其他调控因子的相互作用。
4. **文献名称**:*THAP1 is a nuclear pro-apoptotic factor that links prostate cancer cell response to oxidative stress*
**作者**:Roussigne M, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过THAP1抗体进行免疫荧光和功能实验,证明THAP1在氧化应激下易位至细胞核,激活凋亡相关通路,尤其在前列腺癌细胞中起关键作用。
这些研究均通过THAP1抗体探讨其在疾病机制、基因调控或细胞功能中的角色。
THAP1 (Thanatos-associated protein 1) is a transcription factor belonging to the THAP domain-containing protein family, characterized by a conserved zinc-dependent DNA-binding domain. It regulates gene expression by binding to specific DNA sequences and interacting with protein partners, including HCF-1 (host cell factor 1), to modulate processes like cell proliferation, apoptosis, and epigenetic regulation. Mutations in the THAP1 gene are linked to DYT6 dystonia, a hereditary movement disorder, highlighting its role in neuronal function.
THAP1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions in research. These antibodies, often raised in rabbits or mice, target epitopes within the N-terminal or C-terminal regions of the protein. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect THAP1 in cell lines, tissues, or animal models. Validated antibodies help investigate THAP1's involvement in diseases beyond dystonia, including cancer and neurodevelopmental disorders, where aberrant THAP1 expression or dysfunction has been observed.
Commercial THAP1 antibodies vary in specificity and clonality (monoclonal/polyoclonal), requiring validation via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown to confirm target selectivity. Recent studies also utilize these antibodies to explore THAP1's regulatory mechanisms in chromatin remodeling and its potential as a therapeutic biomarker.
×