| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
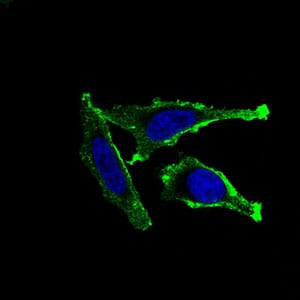
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
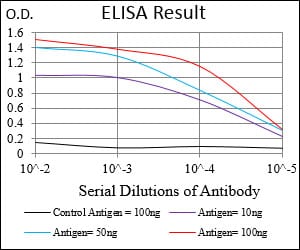
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CR3A; MO1A; CD11B; MAC-1; MAC1A; SLEB6 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3684 |
| clone | 3A10H5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 127.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ITGAM (AA: 623-728) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
1. **"ITGAM is associated with disease susceptibility and renal nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus"**
- **作者**: Nath, S.K., et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究通过全基因组关联分析(GWAS)发现ITGAM基因多态性与系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)的易感性及狼疮肾炎的严重程度显著相关,提示ITGAM在自身免疫反应中的关键作用。
2. **"Anti-ITGAM autoantibodies contribute to neutrophil dysfunction in lupus"**
- **作者**: Kang, Y.M., et al.
- **摘要**: 研究发现SLE患者体内抗ITGAM抗体会干扰中性粒细胞的黏附、迁移和吞噬功能,揭示了此类抗体通过靶向CD11b破坏先天免疫反应的分子机制。
3. **"Autoantibodies against ITGAM as a novel biomarker in early lupus diagnosis"**
- **作者**: Dörner, T., et al.
- **摘要**: 提出抗ITGAM抗体可作为SLE早期诊断的生物标志物,临床队列研究表明其特异性高于传统抗dsDNA抗体,尤其在非典型症状患者中具有潜在应用价值。
4. **"Pathogenic role of anti-CD11b antibodies in lupus nephritis via complement activation"**
- **作者**: Lood, C., et al.
- **摘要**: 实验证实抗ITGAM抗体通过激活补体途径导致肾小球内皮损伤,在狼疮肾炎的病理进程中起直接作用,为靶向ITGAM的治疗策略提供了理论依据。
ITGAM (Integrin Alpha M), also known as CD11b, is a critical subunit of the heterodimeric transmembrane receptor Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18 or αMβ2 integrin). Expressed predominantly on myeloid cells like neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages, it plays a pivotal role in immune responses by mediating cell adhesion, migration, and phagocytosis. ITGAM interacts with ligands such as iC3b, fibrinogen, and ICAM-1. facilitating processes like pathogen clearance, leukocyte recruitment to inflammation sites, and immune cell signaling.
Anti-ITGAM antibodies are essential tools in biomedical research and diagnostics. They are used to detect CD11b expression via flow cytometry, Western blotting, or immunohistochemistry, aiding in immune cell characterization. Dysregulation of ITGAM is linked to autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis) and inflammatory disorders. Genetic variants in ITGAM, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), are associated with increased susceptibility to these conditions. Researchers employ ITGAM-blocking antibodies to study its functional roles in disease models, exploring mechanisms like leukocyte adhesion or complement receptor signaling. Additionally, therapeutic applications are under investigation, targeting ITGAM to modulate immune activation in conditions like sepsis or autoimmune pathologies. These antibodies thus bridge basic research, clinical diagnostics, and potential therapeutic development in immunology.
×