| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
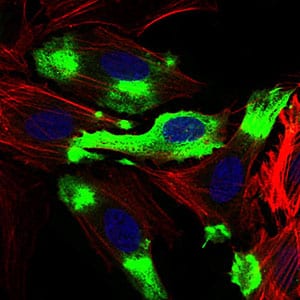
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
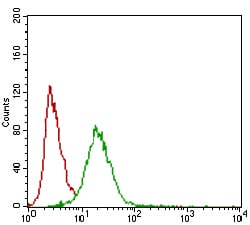
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
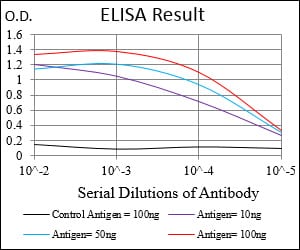
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SIGLEC2; SIGLEC-2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 933 |
| clone | 1A3A11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 95.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD22 (AA: 621-725) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于CD22抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD22 in B-cell malignancies: Bispecific antibodies and beyond*
**作者**:Kreitman RJ, Pastan I
**摘要**:探讨CD22作为B细胞恶性肿瘤治疗靶点的潜力,重点分析双特异性抗体(如结合CD3和CD22)的机制及临床试验进展,强调其在难治性白血病和淋巴瘤中的治疗前景。
2. **文献名称**:*Epratuzumab in autoimmune diseases: A therapeutic monoclonal antibody to CD22*
**作者**:Dorner T, Goldenberg DM
**摘要**:研究抗CD22单抗epratuzumab在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)等自身免疫病中的作用,发现其通过抑制B细胞活化及减少促炎因子分泌缓解疾病活动度,提供临床试验数据支持其安全性。
3. **文献名称**:*Inotuzumab Ozogamicin: A CD22-targeted antibody-drug conjugate for acute lymphoblastic leukemia*
**作者**:Kantarjian HM, DeAngelo DJ
**摘要**:报道抗体药物偶联物(ADC)inotuzumab ozogamicin的Ⅲ期临床试验结果,证明其靶向CD22递送细胞毒素卡奇霉素可显著提高复发/难治性急性淋巴细胞白血病患者的缓解率及生存期。
4. **文献名称**:*CD22 function in B cell signaling pathways*
**作者**:Nitschke L
**摘要**:综述CD22在B细胞信号通路中的调控作用,揭示其通过结合唾液酸配体及与BCR相互作用抑制过度激活,为设计靶向CD22的免疫调节疗法提供理论依据。
以上文献涵盖治疗应用、药物开发及基础机制,反映CD22抗体在肿瘤和免疫疾病中的研究进展。
CD22. a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (Siglec) family, is predominantly expressed on the surface of B cells. It functions as a co-receptor for the B-cell receptor (BCR), modulating B-cell activation, survival, and tolerance through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM)-mediated signaling. CD22’s role in regulating B-cell responses and its restricted expression make it a compelling therapeutic target for B-cell malignancies and autoimmune disorders.
CD22-targeting antibodies have been developed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. In oncology, anti-CD22 antibodies like epratuzumab (a humanized monoclonal antibody) and inotuzumab ozogamicin (an antibody-drug conjugate) are used to treat B-cell lymphomas and acute lymphoblastic leukemia by inducing antibody-dependent cytotoxicity or delivering cytotoxic payloads. In autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), CD22 antibodies aim to suppress pathogenic autoantibody production by depleting overactive B cells.
Recent advances include bispecific antibodies engaging CD22 with other targets (e.g., CD19 or CD20) and chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies incorporating CD22-specific single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) to address antigen escape in relapsed cancers. However, challenges like antigen internalization, heterogeneous CD22 expression, and therapy resistance remain areas of active research. Overall, CD22 antibodies represent a versatile tool in precision medicine, balancing immune modulation and targeted cytotoxicity.
×