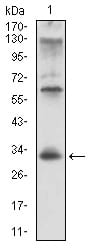
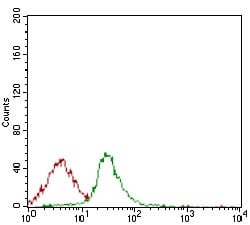
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
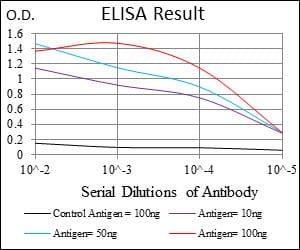
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | II; DHLAG; HLADG; Ia-GAMMA |
| Entrez GeneID | 972 |
| clone | 2D1B11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD74 (AA: 1-106) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CD74抗体的参考文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting CD74 in B-cell malignancies with milatuzumab*
**作者**:Stein R, et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了抗CD74单克隆抗体(milatuzumab)在B细胞恶性肿瘤(如非霍奇金淋巴瘤)中的应用,显示其通过诱导内化和抑制细胞增殖发挥抗肿瘤活性。
2. **文献名称**:*CD74: A multifunctional regulator of immune responses*
**作者**:Stumptner-Cuvelette P, et al.
**摘要**:综述了CD74在MHC II类分子组装和抗原呈递中的核心作用,并讨论其抗体在调节炎症反应及自身免疫疾病中的潜在治疗价值。
3. **文献名称**:*CD74 as a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis*
**作者**:Shi X, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现CD74抗体可阻断MIF(巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子)信号通路,减轻类风湿性关节炎模型中的炎症反应和关节损伤,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
---
以上文献涵盖了CD74抗体在癌症治疗、免疫调节及自身免疫疾病中的应用,均为该领域的重要研究方向。
CD74. also known as invariant chain (Ii), is a transmembrane protein primarily recognized for its role as a chaperone for major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC II) molecules. It facilitates the proper folding, transport, and peptide loading of MHC II in antigen-presenting cells, such as B cells and dendritic cells. Beyond its structural role, CD74 acts as a signaling receptor for macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), a cytokine involved in inflammation, cell survival, and immune regulation. This interaction activates pathways like NF-κB and MAPK, influencing processes such as apoptosis, proliferation, and inflammatory responses.
CD74 is overexpressed in various B-cell malignancies (e.g., lymphoma, leukemia) and autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), making it a therapeutic target. Antibodies targeting CD74 are designed to block its interactions with MIF or disrupt MHC II-mediated antigen presentation. These antibodies are utilized in research to study immune regulation and in diagnostics to detect CD74 expression in pathological tissues. Therapeutically, anti-CD74 antibodies like milatuzumab have been explored in clinical trials for hematologic cancers, leveraging their potential to induce antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) or deliver cytotoxic payloads. Challenges include optimizing specificity and minimizing off-target effects. Overall, CD74 antibodies represent a promising tool for both understanding immune mechanisms and developing targeted therapies.
×