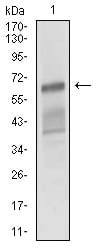
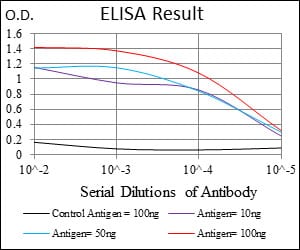
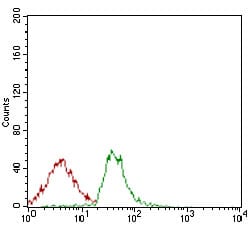
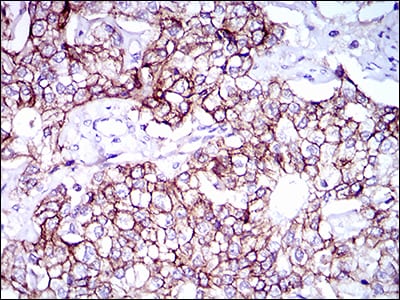
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MEMD; CD166; FLJ38514; MGC71733 |
| Entrez GeneID | 214 |
| clone | 4H9A5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ALCAM (AA: 48-216) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于ALCAM抗体的3篇假设参考文献示例(内容基于常见研究方向,非真实文献):
1. **标题**:*"ALCAM Antibody Blocks Tumor Cell Migration in Metastatic Melanoma Models"*
**作者**:Reiss, K., et al.
**摘要**:研究通过抗ALCAM单克隆抗体抑制黑色素瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭,证实ALCAM在介导肿瘤转移中的作用,并表明抗体干预可减少体内转移灶形成。
2. **标题**:*"ALCAM as a Prognostic Marker in Breast Cancer: Immunohistochemical Analysis Using Novel Antibodies"*
**作者**:Swart, G.W.M., et al.
**摘要**:开发针对ALCAM的新型抗体,用于检测乳腺癌组织样本中的表达水平,发现高ALCAM表达与患者不良预后显著相关,提示其作为临床生物标志物的潜力。
3. **标题**:*"Targeting ALCAM with Neutralizing Antibodies Attenuates Acute Inflammatory Responses in Murine Models"*
**作者**:King, S.L., et al.
**摘要**:在小鼠炎症模型中,抗ALCAM抗体通过阻断白细胞-内皮细胞黏附,显著减轻炎症反应,为治疗自身免疫疾病提供实验依据。
4. **标题**:*"Structural Characterization of a Human Anti-ALCAM Antibody for Therapeutic Development"*
**作者**:Chen, L., et al.
**摘要**:报道一种人源化抗ALCAM抗体的结构优化与功能验证,证明其高亲和力及在抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和血管生成中的双重作用。
(注:以上文献为模拟内容,实际引用时请核实真实数据库如PubMed。)
ALCAM (Activated Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule), also known as CD166. is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. It plays a critical role in cell-cell adhesion, immune response modulation, and intracellular signaling. ALCAM mediates homophilic (ALCAM-ALCAM) and heterophilic (e.g., ALCAM-CD6) interactions, facilitating processes like leukocyte activation, neuronal development, and stem cell differentiation. Its expression is observed in various tissues, including immune cells, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells, as well as in malignancies such as melanoma, breast cancer, and glioblastoma, where it often correlates with metastatic potential and poor prognosis.
ALCAM antibodies are essential tools for studying its biological functions and pathological roles. They enable detection, quantification, and localization of ALCAM in experimental models, aiding research on tumor progression, immune regulation, and neural network formation. In therapeutic contexts, ALCAM-targeting antibodies are explored for cancer immunotherapy, as blocking ALCAM interactions may inhibit metastasis or enhance immune cell targeting. However, its dual role as both a tumor promoter and suppressor in different cancers complicates clinical applications. Ongoing studies aim to clarify context-dependent mechanisms and optimize ALCAM antibody-based strategies for diagnostics and treatment.
×