
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
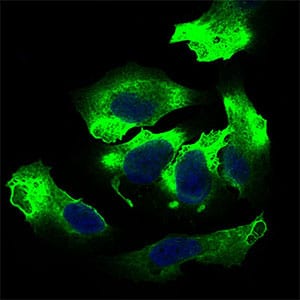
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
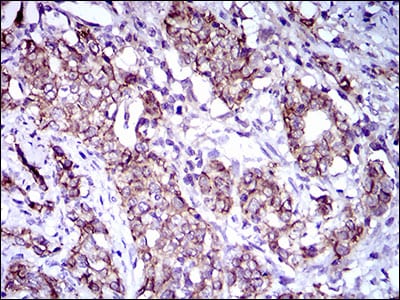
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
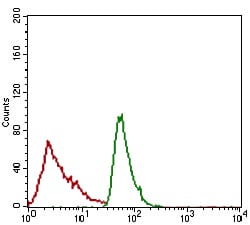
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
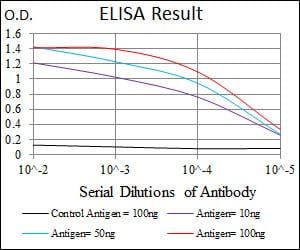
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MEMD; CD166; FLJ38514; MGC71733 |
| Entrez GeneID | 214 |
| clone | 8E12C7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 65.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2a |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ALCAM (AA: 48-216) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于ALCAM抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*ALCAM/CD166: A pleiotropic mediator of cell adhesion, stemness, and cancer progression*
**作者**:Swart GW et al.
**摘要**:该综述总结了ALCAM在肿瘤微环境中的作用,重点讨论其通过抗体靶向调控细胞粘附和干细胞特性的机制,提出ALCAM抗体在抑制肿瘤转移及癌症治疗中的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Development of a humanized anti-ALCAM monoclonal antibody for pancreatic cancer therapy*
**作者**:Chen X et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种人源化ALCAM单克隆抗体,体外实验显示其能特异性结合胰腺癌细胞并抑制侵袭,动物模型中显著延缓肿瘤生长,验证了其作为靶向治疗工具的可行性。
3. **文献名称**:*ALCAM as a biomarker in circulating tumor cells: Detection by novel antibody-based platforms*
**作者**:Müller V et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用新型ALCAM抗体构建CTC检测平台,证实ALCAM高表达与乳腺癌患者不良预后相关,提示其作为液体活检标志物的临床价值。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性概括,实际引用时需核对原文准确性。)
The Activated Leukocyte Cell Adhesion Molecule (ALCAM), also known as CD166. is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF). It mediates cell-cell adhesion through homophilic (ALCAM-ALCAM) or heterophilic (ALCAM-CD6) interactions, playing roles in immune regulation, neural development, and cancer progression. ALCAM is expressed in activated leukocytes, endothelial cells, and various epithelial tissues, where it participates in T-cell activation, leukocyte trafficking, and tissue organization. Its involvement in pathological processes, particularly cancer metastasis and inflammatory diseases, has made it a research focus.
ALCAM antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry, and Western blotting to assess ALCAM levels in tissues or cells. In cancer research, elevated ALCAM expression correlates with aggressive phenotypes in melanoma, breast, and prostate cancers, suggesting its potential as a prognostic biomarker. Conversely, in some contexts, ALCAM acts as a tumor suppressor, highlighting context-dependent roles.
Therapeutic ALCAM-targeting antibodies are under exploration. For example, blocking ALCAM-CD6 interactions may modulate immune responses in autoimmune diseases or enhance antitumor immunity. However, challenges remain in understanding its dual roles and ensuring target specificity. Overall, ALCAM antibodies bridge basic research and clinical applications, offering insights into disease mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.
×