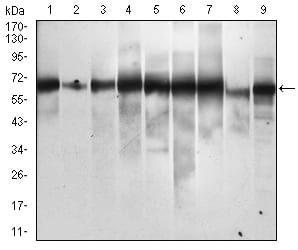
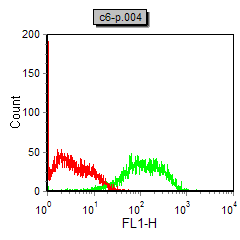
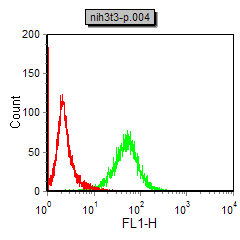
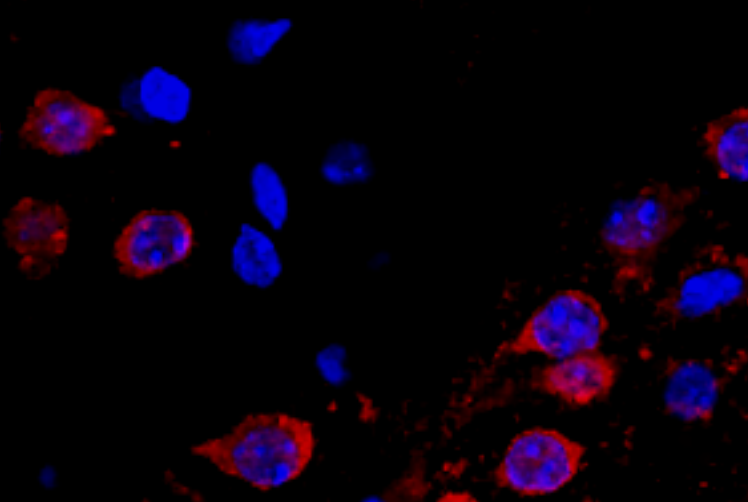
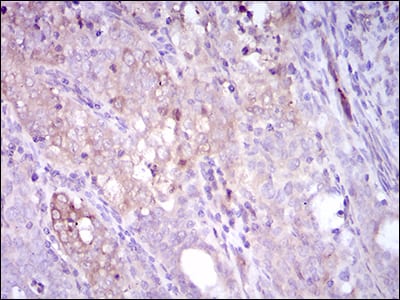
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
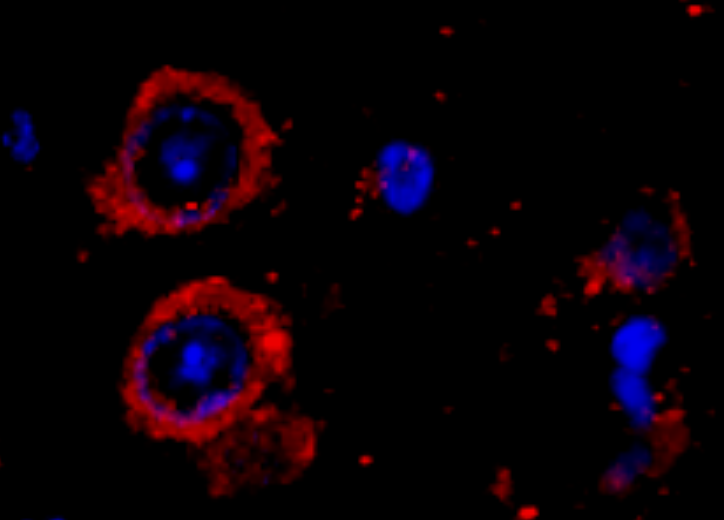
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
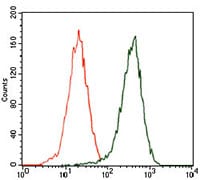
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
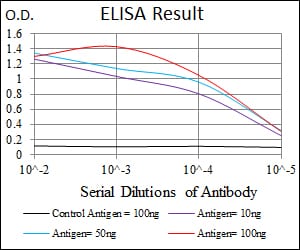
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p60; p62; A170; OSIL; PDB3; ZIP3; p62B |
| Entrez GeneID | 8878 |
| clone | 5H7E2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human SQSTM1 (AA: 232-356) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇与SQSTM1/p62抗体相关的文献摘要信息:
1. **文献名称**:*p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy*
**作者**:Pankiv S et al. (2007)
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,利用SQSTM1抗体验证了p62蛋白通过LC3结合域与自噬标记物LC3的相互作用,揭示了其在介导泛素化蛋白聚集体自噬降解中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*SQSTM1 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis*
**作者**:Fecto F et al. (2011)
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫组化技术(使用SQSTM1抗体),研究发现ALS患者中SQSTM1基因突变导致p62蛋白异常聚集,提示其与运动神经元变性疾病的病理关联。
3. **文献名称**:*Defective recognition of LC3B by mutant SQSTM1/p62 implicates impairment of autophagy as a pathogenic mechanism in ALS-FTD*
**作者**:Goode A et al. (2016)
**摘要**:该文献利用SQSTM1抗体进行细胞定位分析,发现ALS-FTD相关突变破坏了p62与LC3B的结合能力,导致自噬功能障碍和神经细胞中异常蛋白积累。
4. **文献名称**:*Validation of commercial SQSTM1/p62 antibodies for neurodegenerative disease research*
**作者**:Thompson AG et al. (2020)
**摘要**:研究系统比较了多种市售SQSTM1抗体的特异性,通过敲除细胞系验证其在人脑组织中的可靠性,为神经退行性疾病中p62病理沉积的检测提供方法学支持。
*提示*:实际引用时建议通过PubMed或期刊官网核对文献详细信息及DOI编号。
×