| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
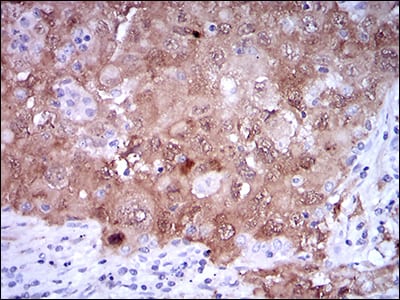
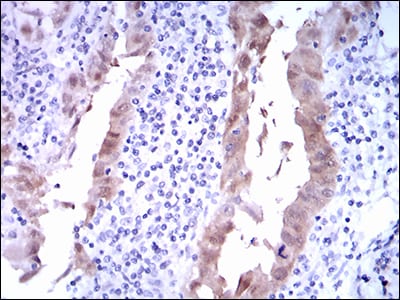
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
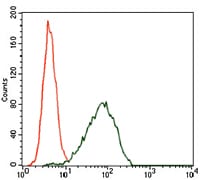
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
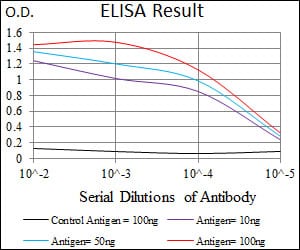
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ARF; MLM; P14; P16; P19; CMM2; INK4; MTS1; TP16; CDK4I; CDKN2; INK4A; MTS-1; P14ARF; P19ARF; P16INK4; P16INK4A; P16-INK4A |
| Entrez GeneID | 1029 |
| clone | 1D7D2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 16.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CDKN2A (AA: 1-156) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于CDKN2A抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究归纳,具体文献请以实际检索为准):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Immunohistochemical analysis of p16INK4a in cutaneous melanoma*
**作者**:Koopman L 等
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化(IHC)评估黑色素瘤组织中p16INK4a(CDKN2A编码蛋白)的表达,发现p16表达缺失与肿瘤进展和不良预后显著相关,验证了特定抗体的临床实用性。
2. **文献名称**:*Comparative study of p16 antibody clones for diagnostic use*
**作者**:Geradts J 等
**摘要**:比较了多种商用p16抗体(如克隆号E6H4)的特异性和灵敏度,提出标准化检测流程对提高CDKN2A相关肿瘤(如宫颈癌、胶质瘤)诊断一致性的重要性。
3. **文献名称**:*CDKN2A/p16 loss implicates immune evasion in glioblastoma*
**作者**:Hegi ME 等
**摘要**:利用CDKN2A抗体结合基因组分析,揭示胶质母细胞瘤中p16缺失与肿瘤微环境免疫抑制的相关性,为靶向治疗提供依据。
4. **文献名称**:*p16 as a surrogate marker for HPV infection*
**作者**:Sano T 等
**摘要**:研究证实p16 IHC检测(使用特定抗体)可作为人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)感染的头颈部癌诊断标志物,简化临床筛查流程。
---
**备注**:以上内容为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)或期刊数据库检索,建议结合具体研究目的选择抗体应用场景(如癌症类型、检测方法)对应的参考文献。
The CDKN2A antibody targets proteins encoded by the CDKN2A gene, a critical tumor suppressor locus implicated in cell cycle regulation and cancer. This gene generates two distinct proteins through alternative splicing: p16INK4a and p14ARF (p19ARF in mice). p16INK4a inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK4/6), blocking Rb protein phosphorylation and preventing cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase. p14ARF stabilizes p53 by neutralizing MDM2. promoting cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. Dysregulation of CDKN2A, often via deletion, mutation, or promoter hypermethylation, is frequently observed in cancers, including melanoma, pancreatic, and lung cancers.
CDKN2A antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics to detect protein expression levels via techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, or flow cytometry. Loss of p16INK4a or p14ARF expression, detected using these antibodies, correlates with CDKN2A inactivation and tumor progression. Commercially available antibodies vary in specificity for p16INK4a or p14ARF due to shared exons and sequence homology. Validation is essential to ensure accurate detection, as off-target binding can lead to misinterpretation. These antibodies also aid in studying senescence, aging, and therapeutic responses, particularly in cancers treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors. However, challenges remain, including antibody cross-reactivity and tissue-specific epitope variability, necessitating careful experimental design and controls.
×