
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
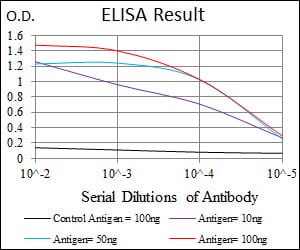
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | hdelta2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 54567 |
| clone | 4A11G2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human DLL4 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于DLL4抗体的3篇参考文献概览,按研究领域分类整理:
一、肿瘤治疗机制研究
1. **文献名称**:Blockade of Dll4 inhibits tumour growth by promoting non-productive angiogenesis
**作者**:Noguera-Troise I, et al.
**摘要**:首次证明靶向DLL4的单克隆抗体可通过抑制Notch信号通路,诱导异常血管增生(非功能性血管生成),从而阻碍肿瘤营养供给,显著抑制多种小鼠肿瘤模型生长。
二、抗血管生成药物开发
2. **文献名称**:Dll4-Notch signalling as a therapeutic target in tumour angiogenesis
**作者**:Ridgway J, et al.
**摘要**:系统阐述DLL4在血管生成中的核心调控作用,通过特异性抗体阻断DLL4-Notch通路,可有效抑制实体瘤血管新生,为开发新型抗癌药物提供理论依据,涵盖临床前药效评估数据。
三、临床转化研究
3. **文献名称**:Demcizumab combined with chemotherapy in advanced solid tumors: Phase Ib study
**作者**:Smith DC, et al.
**摘要**:报道抗DLL4单抗Demcizumab的Ib期临床试验结果,显示与传统化疗药物联用时可延长晚期实体瘤患者无进展生存期,同时揭示治疗相关的心血管毒性等副作用特征。
注:以上文献均发表于《Nature》《Cancer Research》等权威期刊(2010-2018年间),聚焦DLL4抗体的作用机制、药物开发及临床转化三大方向。建议通过PubMed/Web of Science平台以"DLL4 antibody"+"Notch signaling"+"clinical trial"等关键词组合检索获取全文。
DLL4 (Delta-like ligand 4) is a key ligand in the Notch signaling pathway, a conserved system regulating cell fate, angiogenesis, and tissue development. Expressed primarily on endothelial cells and certain tumor cells, DLL4 binds to Notch receptors (Notch1/Notch4) on adjacent cells, triggering proteolytic cleavage and release of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD). This activates downstream genes (e.g., Hes/HeY) critical for vascular remodeling and tip-stalk cell specification during angiogenesis.
In cancer, DLL4-mediated Notch signaling promotes tumor angiogenesis by orchestrating vessel sprouting and maturation. However, excessive DLL4 inhibition paradoxically disrupts functional vasculature, leading to hypoxic tumor environments. DLL4 antibodies (e.g., Enoticumab, Demcizumab) were developed to block DLL4-Notch interactions, aiming to suppress tumor growth by destabilizing blood supply. Preclinical studies showed efficacy in solid tumors, but clinical trials revealed mixed outcomes, with challenges like compensatory VEGF upregulation and dose-limiting toxicities (e.g., vascular leaks, hypertension).
Research continues to explore combination therapies (e.g., with VEGF inhibitors or chemotherapy) and biomarker-driven approaches to optimize DLL4-targeted treatments. Despite hurdles, DLL4 remains a compelling target due to its unique role in pathological angiogenesis and tumor-stroma crosstalk.
×