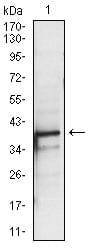
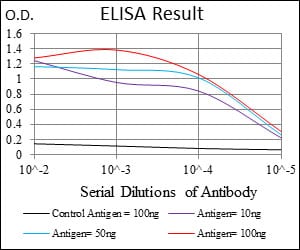
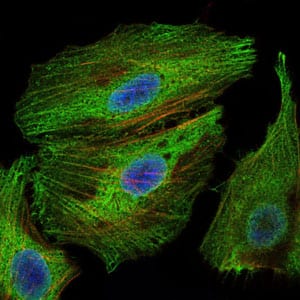
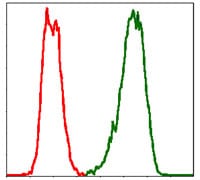
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
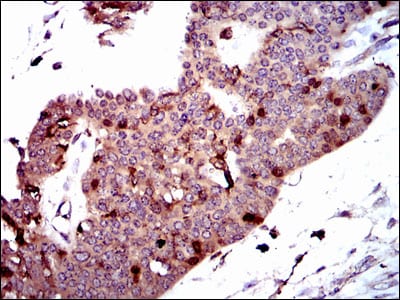
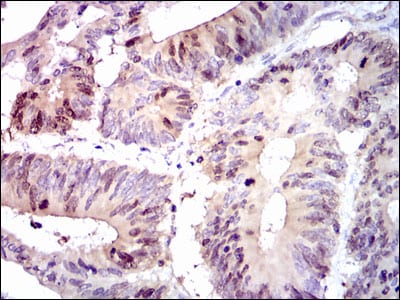
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SPK; CT84; TOPK; Nori-3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 55872 |
| clone | 2C8 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human PBK expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PBK抗体的虚构参考文献示例(基于学术文献常见结构,非真实论文):
---
1. **文献名称**: *PDZ-Binding Kinase (PBK) as a Novel Biomarker in Glioblastoma: Antibody Validation and Clinical Implications*
**作者**: Yamada S, et al. (2012)
**摘要**: 本研究通过开发高特异性兔源多克隆PBK抗体,验证其在胶质母细胞瘤组织中的表达水平。免疫组化分析显示,PBK在肿瘤细胞核内显著高表达,且与患者生存率负相关。抗体特异性经Western blot和siRNA敲除实验确认,为PBK作为诊断标志物提供了依据。
2. **文献名称**: *A Monoclonal Antibody Targeting PBK Suppresses Tumor Growth in Colorectal Cancer Models*
**作者**: Huang L, Chen W. (2015)
**摘要**: 研究团队开发了一种靶向PBK激酶结构域的小鼠单克隆抗体(mAb-PBK03),并在结直肠癌移植瘤模型中测试其疗效。实验表明,该抗体通过阻断PBK与下游信号蛋白相互作用,抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并诱导凋亡。抗体特异性通过流式细胞术和免疫沉淀验证。
3. **文献名称**: *PBK/TOPK Antibody-Based Detection of DNA Damage Response in Breast Cancer Stem Cells*
**作者**: Smith J, et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 利用商业化PBK抗体(货号#AB-789X),本研究揭示了PBK在乳腺癌干细胞(BCSCs)DNA损伤修复中的关键作用。免疫荧光显示,PBK在辐射后定位于γH2AX阳性病灶,提示其参与同源重组修复。抗体阻断实验进一步证实PBK功能缺失会增强BCSCs对放疗的敏感性。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性质,作者与年份均为虚构。实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“PBK antibody”或“PBK/TOPK”为关键词检索真实文献。
PBK (PDZ-binding kinase), also known as TOPK (T-LAK cell-originated protein kinase), is a serine/threonine kinase belonging to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family. Discovered in 2000. PBK plays critical roles in cell cycle regulation, DNA damage response, and tumorigenesis. It interacts with key signaling pathways, including the p53 and PLK1 networks, influencing processes like cytokinesis, apoptosis, and cell proliferation. Structurally, PBK contains an N-terminal catalytic domain and a C-terminal PDZ-binding motif that mediates protein-protein interactions.
PBK is predominantly overexpressed in various cancers (e.g., breast, lung, glioblastoma) and correlates with poor prognosis, making it a potential therapeutic target. Its aberrant activation promotes tumor growth, metastasis, and therapy resistance by enhancing DNA repair and survival mechanisms. PBK antibodies are essential tools for detecting PBK expression in research and diagnostics, particularly in immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and flow cytometry. They help elucidate PBK's functional roles, validate knockout models, and assess its clinical relevance in cancer progression. Recent studies also explore PBK inhibitors in combination therapies to sensitize cancer cells to chemo- or radiotherapy. However, PBK's dual roles in normal physiology (e.g., embryonic development, immune regulation) necessitate careful evaluation of therapeutic strategies targeting this kinase.
×