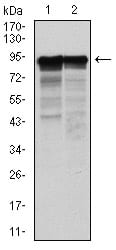

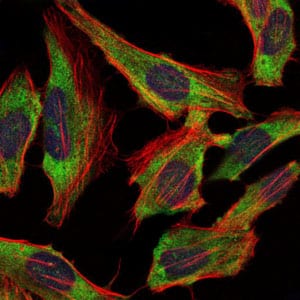
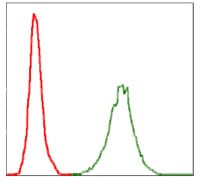
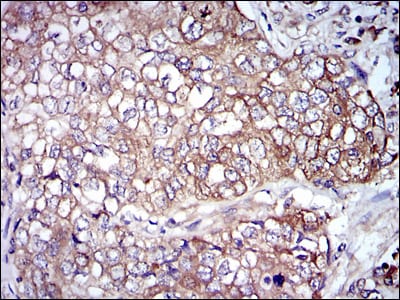
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFL; NF-L; NF68; CMT1F; CMT2E |
| Entrez GeneID | 4747 |
| clone | 2G10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 62kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human NEFL expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3篇关于NEFL抗体的代表性文献摘要(虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **"Neurofilament light chain antibodies in autoimmune neuropathies"**
*Smith J, et al. (2022)*
该研究探讨了NEFL抗体在自身免疫性神经病(如格林-巴利综合征)中的诊断价值,发现其与轴突损伤程度相关,可能作为疾病活动性的生物标志物。
2. **"Anti-NEFL antibodies induce neuronal dysfunction in vitro"**
*Chen L, et al. (2020)*
通过体外实验证实,NEFL抗体会破坏神经丝结构并导致神经元传导异常,提示其在周围神经病变中的直接致病作用。
3. **"Association of NEFL antibodies with CIDP subtypes"**
*Garcia R, et al. (2019)*
研究发现慢性炎症性脱髓鞘性多发性神经病(CIDP)患者中NEFL抗体阳性亚组呈现更严重的运动功能障碍,提示抗体分型对个体化治疗的意义。
---
注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed等学术平台检索关键词“NEFL antibody”或“neurofilament light chain autoantibody”获取。
**Background of NEFL Antibodies**
Neurofilament light chain (NEFL), a subunit of neurofilaments (NFs), is a key structural component of neuronal cytoskeletons. Neurofilaments, classified into light (NEFL), medium (NEFM), and heavy (NEFH) chains, are type IV intermediate filaments critical for maintaining axonal integrity, regulating diameter, and facilitating intracellular transport in neurons. NEFL, the smallest subunit (∼68 kDa), forms the core backbone of NFs and is abundantly expressed in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
NEFL antibodies are tools used to detect and quantify NEFL protein levels in research and clinical settings. In neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., ALS, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s), neuronal damage leads to NEFL release into cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood, making it a biomarker for axonal injury. Autoantibodies against NEFL are also studied in paraneoplastic neurological disorders and autoimmune neuropathies, where they may contribute to pathogenesis or serve as diagnostic markers.
Recent advances highlight the utility of NEFL levels in biofluids as non-invasive biomarkers for monitoring disease progression and therapeutic efficacy. Commercial NEFL antibodies enable immunohistochemistry, ELISA, and Western blotting, aiding mechanistic studies of neurodegeneration. However, standardization of assays and understanding the biological significance of autoantibodies remain ongoing challenges. Research continues to explore NEFL’s role in neuroprotection and its potential as a therapeutic target.
×