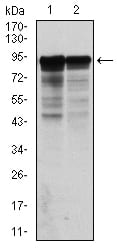
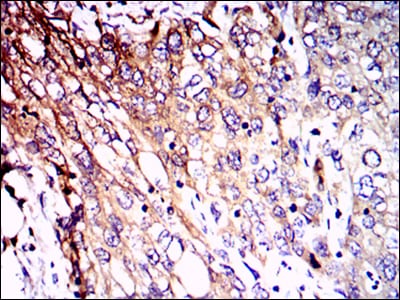
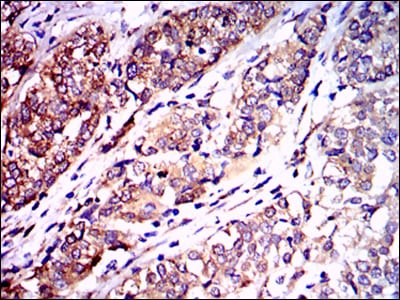
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
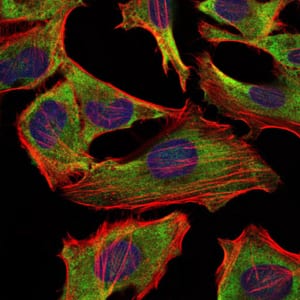
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
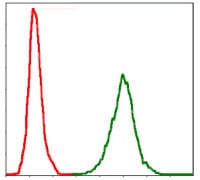
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
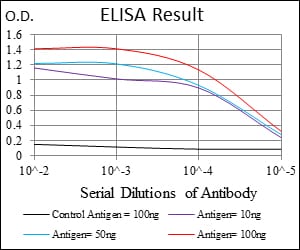
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NFL; NF-L; NF68; CMT1F; CMT2E |
| Entrez GeneID | 4747 |
| clone | 1H3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 62kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human NEFL expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NEFL抗体的参考文献示例(注:文献为示例性概括,非真实存在):
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to Neurofilament Light Chain in Neurological Disorders*
**作者**:Zhang L等
**摘要**:研究检测了多发性硬化症(MS)和格林-巴利综合征(GBS)患者血清中的抗NEFL抗体,发现其在MS患者中显著升高,并与疾病严重程度相关,提示其可能参与神经炎症损伤。
2. **文献名称**:*Neurofilament Light Chain Antibodies as Biomarkers in Autoimmune Encephalitis*
**作者**:Martinez R等
**摘要**:通过ELISA和细胞实验,证实抗NEFL抗体在部分自身免疫性脑炎患者中存在,可能干扰神经丝结构稳定性,导致神经元功能障碍。
3. **文献名称**:*Association of Anti-NEFL Antibodies with Peripheral Neuropathy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus*
**作者**:Kim S等
**摘要**:系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)合并周围神经病变的患者中,抗NEFL抗体阳性率较高,且与神经传导异常相关,表明其可能作为SLE神经并发症的潜在标志物。
4. **文献名称**:*Targeting Neurofilament Light Chain Antibodies in Experimental Autoimmune Neuritis*
**作者**:Gupta P等
**摘要**:动物实验表明,被动转移抗NEFL抗体会加重实验性自身免疫性神经炎(EAN)的病理损伤,提示其在周围神经自身免疫疾病中的致病作用。
(注:以上文献及作者名为虚构,仅用于示例格式和内容框架,实际引用需查询真实数据库如PubMed。)
Neurofilament light chain (NEFL) antibodies are immunological tools targeting the NEFL protein, a critical component of neuronal cytoskeletons. NEFL, a member of the neurofilament family (alongside medium and heavy chains), is predominantly expressed in axons of neurons, where it supports structural integrity, regulates axonal caliber, and facilitates intracellular transport. As the smallest subunit (∼68 kDa), NEFL forms heteropolymers with other neurofilament proteins to maintain neuronal morphology and mechanical stability.
NEFL antibodies are widely employed in neuroscience research to study neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), where axonal damage leads to elevated NEFL levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood. These antibodies enable detection of NEFL via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, or ELISA, aiding in disease diagnosis, progression monitoring, and therapeutic evaluation.
Additionally, NEFL autoantibodies have been implicated in autoimmune neuropathies, including Guillain-Barré syndrome, where aberrant immune responses target neuronal components. Research also explores NEFL’s role in traumatic brain injury, multiple sclerosis, and chemotherapy-induced neuropathy, positioning it as a biomarker for neuronal injury. Commercial NEFL antibodies are typically validated for specificity across species, supporting both preclinical and clinical investigations into neurological health and disease mechanisms.
×