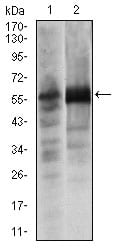
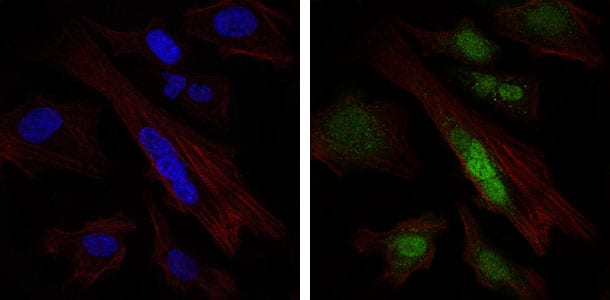
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
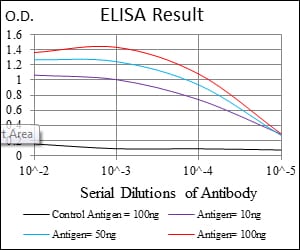
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CMD1; SRA1; CMPD1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6662 |
| clone | 1B11 |
| WB Predicted band size | 56kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human SOX9 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于 **SOX9抗体** 的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"A monoclonal antibody against Sox9 reveals its role in cartilage development"*
**作者**:Bi, W., et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种特异性识别SOX9蛋白的单克隆抗体,并验证其在胚胎发育中软骨形成的关键作用。通过免疫组化和Western blot分析,揭示了SOX9在软骨细胞分化中的动态表达模式。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Sox9 is required for determination of the chondrogenic cell lineage in the cranial neural crest"*
**作者**:Mori-Akiyama, Y., et al.
**摘要**:利用SOX9抗体进行免疫荧光和染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP),研究发现SOX9在颅神经嵴细胞向软骨细胞谱系分化中起决定性作用,并调控下游靶基因(如Col2a1)的表达。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"SOX9 is a prostate cancer tumor suppressor and master regulator of lineage plasticity"*
**作者**:Thomsen, M.K., et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析前列腺癌组织,发现SOX9表达缺失与肿瘤进展相关。研究利用特异性抗体证实SOX9通过抑制上皮-间质转化(EMT)维持细胞分化,具有肿瘤抑制功能。
---
4. **文献名称**:*"Validation of a polyclonal anti-SOX9 antibody for functional studies in zebrafish"*
**作者**:Yan, Y.L., et al.
**摘要**:该文献验证了一种兔源多克隆SOX9抗体的跨物种适用性(包括斑马鱼和小鼠),证明其可用于原位杂交和蛋白定位,并揭示了SOX9在脊椎动物性别决定和器官发育中的保守性。
---
这些文献涵盖了SOX9抗体在基础研究(如发育生物学)和疾病模型(如癌症)中的应用,涉及抗体开发、验证及功能机制解析。
SOX9 antibodies are essential tools in biomedical research for detecting and analyzing the SOX9 protein, a transcription factor belonging to the SOX (SRY-related HMG-box) family. SOX9 plays pivotal roles in embryonic development, particularly in chondrogenesis, sex determination, and neural crest cell differentiation. It regulates gene expression by binding to DNA through its HMG domain, influencing cell fate and tissue morphogenesis. Mutations in the SOX9 gene are linked to congenital disorders like campomelic dysplasia, characterized by skeletal malformations and sex reversal. In cancer, SOX9 exhibits context-dependent roles, acting as an oncogene in some malignancies (e.g., prostate cancer, glioblastoma) or a tumor suppressor in others (e.g., skin squamous cell carcinoma).
SOX9 antibodies are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry to study protein expression, localization, and function. These antibodies help identify SOX9 in tissue sections, cell lines, or animal models, aiding research on developmental biology, disease mechanisms, and regenerative medicine. Validation of SOX9 antibodies is critical, as specificity can vary between clones and applications. Commercial antibodies are often raised against epitopes within the N-terminal transactivation domain or the C-terminal region. Researchers rely on SOX9 antibodies to explore its regulatory networks, interactions with signaling pathways (e.g., Wnt/β-catenin, TGF-β), and therapeutic targeting potential in developmental disorders and cancers.
×