| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
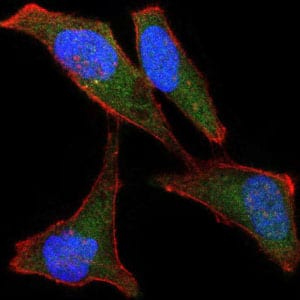
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
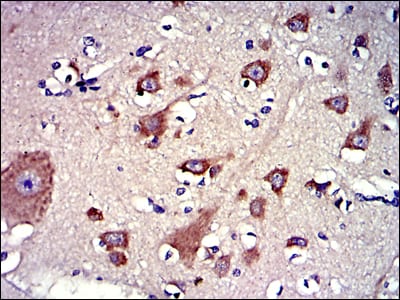
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
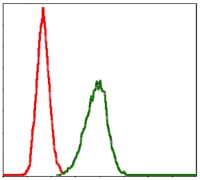
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
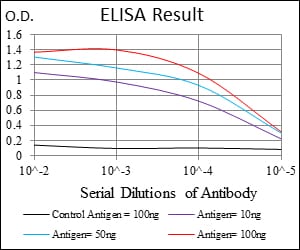
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BPIFB1; LPLUNC1; MGC14597; C20orf114 |
| Entrez GeneID | 92747 |
| clone | 2A5 |
| WB Predicted band size | 52kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LPlunc1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于LPLUNC1(BPIFB1)抗体的3篇参考文献概览,涵盖其在疾病研究和功能分析中的应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*LPLUNC1 inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and migration through downregulation of the JNK signaling pathway*
**作者**:Li Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用LPLUNC1特异性抗体验证蛋白在鼻咽癌细胞中的表达,发现其通过抑制JNK通路抑制肿瘤侵袭,提示其作为抑癌基因的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Expression and functional analysis of BPIFB1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma*
**作者**:Chen X. et al.
**摘要**:通过LPLUNC1抗体检测口腔鳞癌组织样本,发现其低表达与预后不良相关,体外实验证实其过表达可抑制肿瘤细胞增殖和迁移。
3. **文献名称**:*The role of LPLUNC1 in innate immunity of the upper respiratory tract*
**作者**:Bingle C.D. et al.
**摘要**:利用LPLUNC1抗体定位蛋白在呼吸道黏膜分泌细胞中的表达,揭示其通过结合脂多糖调控局部免疫反应,可能与慢性炎症疾病相关。
---
**说明**:LPLUNC1(BPIFB1)属于BPI蛋白家族,相关研究多聚焦于其在肿瘤抑制、免疫调节及感染防御中的作用,上述文献均通过抗体检测明确其表达模式及功能机制。若需具体DOI或发表年份,可进一步补充检索。
The LPLUNC1 (Long Palate, Lung, and Nasal Epithelium Carcinoma-Associated Protein 1) antibody is a tool used to study the BPIFA1 protein, encoded by the *BPIFA1* gene. LPLUNC1. also known as SPLUNC1 or BPIFA1. belongs to the BPI fold-containing protein family, which shares structural homology with bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI). It is predominantly expressed in the upper respiratory tract, oral mucosa, and salivary glands, playing roles in innate immunity and mucosal defense. The protein is implicated in antimicrobial activity, inflammation modulation, and maintenance of epithelial barrier integrity.
Antibodies against LPLUNC1 are utilized to investigate its expression patterns and functional mechanisms in diseases such as chronic rhinosinusitis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD. Studies suggest LPLUNC1 interacts with pathogens, regulates ion transport, and influences airway surface liquid composition. Its dysregulation is linked to chronic inflammation and infection susceptibility.
These antibodies enable detection via Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or ELISA, aiding in biomarker research and therapeutic target exploration. Recent work also examines LPLUNC1’s potential in cancer, particularly head and neck malignancies, where it may suppress tumorigenesis. Overall, LPLUNC1 antibodies are critical for unraveling its dual role in host defense and disease pathology.
×