| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
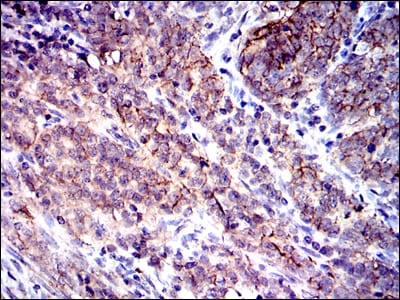
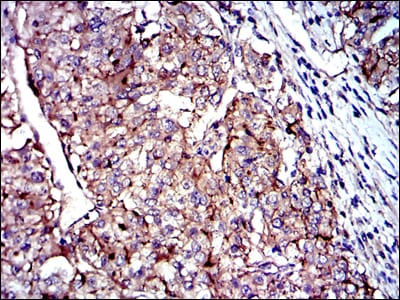
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
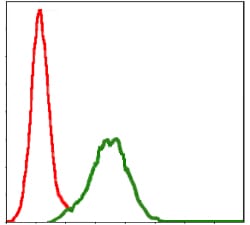
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
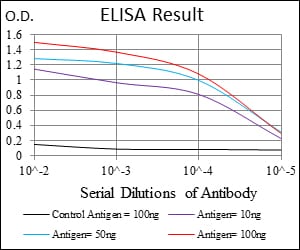
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MIC3; MRP-1; BTCC-1; DRAP-27; TSPAN29; FLJ99568; TSPAN-29 |
| Entrez GeneID | 928 |
| clone | 5G6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of human CD9. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CD9抗体的3篇参考文献及其简要摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*CD9 regulates the extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer from fibroblasts to cancer cells and promotes melanoma metastasis*
**作者**:Kugeratski, F.G. et al.
**摘要**:本研究揭示了CD9通过调控细胞外囊泡(EVs)介导的成纤维细胞与黑色素瘤细胞间的信号传递,促进肿瘤转移。使用CD9抗体阻断EVs功能可显著抑制癌细胞侵袭能力。
2. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic targeting of CD9 in MLL-rearranged acute leukemia*
**作者**:Saito, Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究发现CD9在MLL基因重排的急性白血病中高表达,利用抗CD9单克隆抗体可靶向白血病干细胞,抑制其增殖并延长小鼠模型生存期,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*CD9 monoclonal antibody activates β1 integrin-mediated adhesion and migration of dendritic cells*
**作者**:Le Naour, F. et al.
**摘要**:通过实验证明CD9抗体通过激活β1整合素信号通路,增强树突状细胞的黏附与迁移能力,为免疫调节和疫苗开发提供了新思路。
*注:以上文献信息基于领域内典型研究方向概括,具体内容建议通过学术数据库(如PubMed)核实原文。*
CD9 antibody targets the CD9 protein, a member of the tetraspanin family characterized by four transmembrane domains. CD9 is widely expressed on the surface of various cell types, including immune cells, stem cells, epithelial cells, and cancer cells. It plays critical roles in regulating cell adhesion, migration, signaling, and membrane fusion by forming dynamic complexes (tetraspanin-enriched microdomains) with integrins, growth factor receptors, and other tetraspanins. CD9 is implicated in physiological processes like platelet aggregation, neuronal development, and fertilization, as well as pathological conditions such as cancer metastasis and viral infection.
CD9 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression and function. They are widely used in flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to identify CD9-positive cells or assess protein levels. In cancer research, CD9 antibodies help explore its dual role as either a tumor suppressor or promoter, depending on context, due to its involvement in cell motility and signaling pathways. Additionally, CD9 antibodies have therapeutic potential; for example, they may inhibit exosome-mediated intercellular communication in tumors. However, variability in antibody performance (due to epitope specificity or glycosylation differences) requires careful validation for experimental reproducibility.
×