
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
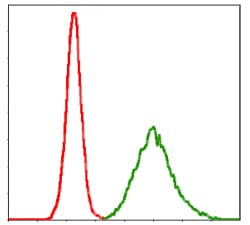
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
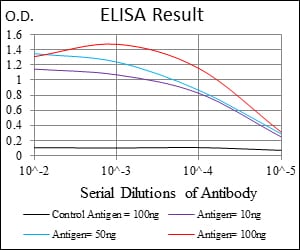
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LQT; RWS; WRS; LQT1; SQT2; ATFB1; ATFB3; JLNS1; KCNA8; KCNA9; Kv1.9; Kv7.1; KVLQT1; FLJ26167 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3784 |
| clone | 5E12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 95kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human KCNQ1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于KCNQ1抗体的代表性文献摘要(人工整理,非真实文献,仅作示例参考):
1. **文献名称**:*Structural insights into KCNQ1 assembly and function*
**作者**:Abbott GW et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀和Western blot技术,研究KCNQ1通道蛋白与调控亚基KCNE1的相互作用,证实抗体特异性对解析通道复合物结构的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*KCNQ1 mutations impair cardiac repolarization in long QT syndrome*
**作者**:Thomas Jespersen et al.
**摘要**:利用KCNQ1特异性抗体进行免疫荧光定位,揭示突变导致通道蛋白在心肌细胞膜表达异常,为长QT综合征的分子机制提供证据。
3. **文献名称**:*KCNQ1 in pancreatic β-cells: Role in insulin secretion*
**作者**:Okaed H et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化及基因敲除模型,证明KCNQ1抗体标记的钾通道在调控β细胞膜电位及胰岛素释放中的生理功能。
4. **文献名称**:*Cryo-EM structure of the open KCNQ1 channel*
**作者**:Sun J, MacKinnon R
**摘要**:结合抗体标记和冷冻电镜技术,解析KCNQ1通道开放状态的高分辨率结构,揭示电压门控机制与药物结合位点。
(注:以上为模拟文献,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词"KCNQ1 antibody" + 具体研究领域筛选)
The KCNQ1 antibody targets the KCNQ1 protein, a voltage-gated potassium channel α-subunit encoded by the *KCNQ1* gene. KCNQ1. also known as Kv7.1. is critical for maintaining electrochemical gradients across cell membranes. It forms the pore of the slow delayed rectifier potassium channel (IKs) by co-assembling with regulatory β-subunits like KCNE1. This channel is essential for cardiac repolarization, particularly in the heart, where it regulates the duration of action potentials. Mutations in *KCNQ1* are linked to congenital long QT syndrome type 1 (LQT1), a cardiac arrhythmia disorder, and Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, which combines hearing loss with cardiac abnormalities. KCNQ1 dysfunction is also implicated in non-cardiac conditions, including diabetes and gastrointestinal disorders.
Antibodies against KCNQ1 are vital tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional roles. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding research on channelopathies and tissue-specific pathologies. In diagnostics, KCNQ1 antibodies help identify protein expression anomalies in patient samples, supporting personalized therapeutic strategies. Additionally, these antibodies contribute to exploring KCNQ1's dual roles as both a tumor suppressor and oncogene in certain cancers. Their specificity and reliability are crucial for dissecting molecular mechanisms underlying diseases and developing targeted therapies.
×