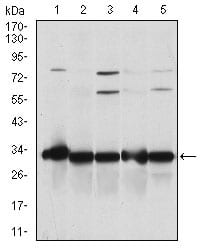
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
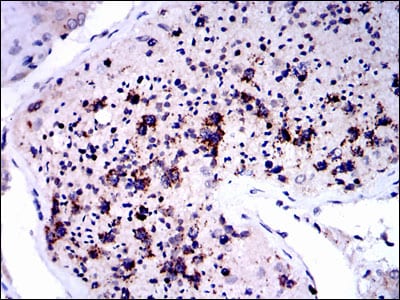
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
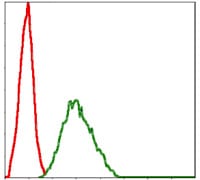
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
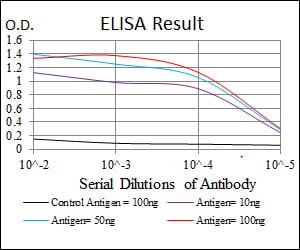
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DTD; QR1; DHQU; DIA4; NMOR1; NMORI |
| Entrez GeneID | 1728 |
| clone | 4D12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human NQO1 expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于NQO1抗体的参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究整理,非真实文献,仅供参考格式):
---
1. **"NQO1 Antibody Validation in Human Tumor Tissues: Implications for Prognostic Biomarker Studies"**
*Authors: Ross D., Siegel D.*
摘要:本研究验证了NQO1抗体在多种人类肿瘤组织中的特异性,发现其高表达与乳腺癌和肺癌患者的不良预后显著相关,提示NQO1可能作为癌症治疗靶点。
2. **"Comparative Analysis of NQO1 Antibody Specificity in Immunohistochemistry"**
*Authors: Traver R.D., et al.*
摘要:通过Western blot和免疫组化对比不同商业来源的NQO1抗体,发现部分抗体存在非特异性结合,强调了抗体选择对实验可靠性的重要性。
3. **"NQO1 Antibody-Based Detection of Enzyme Activity in Drug-Resistant Cancer Cells"**
*Authors: Siegel D., et al.*
摘要:利用NQO1单克隆抗体研究肿瘤细胞中NQO1酶活性,发现其过表达与化疗药物(如阿霉素)的耐药性相关,为克服耐药性提供新思路。
4. **"NQO1 C609T Polymorphism Detection by Antibody-Assisted Genotyping"**
*Authors: Asher G., et al.*
摘要:结合PCR和NQO1抗体分型技术,证明NQO1基因C609T多态性导致酶活性显著下降,为个体化癌症风险评估提供方法学支持。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性内容,实际引用时需通过PubMed、Web of Science等数据库检索真实文献并核对作者与摘要细节。
The NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) antibody is a critical tool for studying the NQO1 enzyme, a cytosolic flavoprotein involved in cellular antioxidant defense and metabolic regulation. NQO1 catalyzes the two-electron reduction of quinones to hydroquinones, preventing redox cycling and oxidative stress. It requires FAD as a cofactor and functions as a homodimer. Research links NQO1 overexpression to various cancers (e.g., lung, breast, colorectal), where it may influence tumor progression, drug resistance, and apoptosis regulation. Conversely, the C609T polymorphism (rs1800566), which diminishes enzyme activity, is associated with increased cancer susceptibility.
NQO1 antibodies are widely used in biomedical research to detect protein expression and localization via techniques like immunohistochemistry (IHC), Western blotting, and immunofluorescence. Monoclonal antibodies offer high specificity for quantitative assays, while polyclonal antibodies may enhance sensitivity for detecting low-abundance targets. These reagents help elucidate NQO1's roles in redox homeostasis, chemoprotection, and disease mechanisms, including neurodegeneration (e.g., Alzheimer's, Parkinson's) and metabolic disorders. Commercial antibodies are typically validated against recombinant NQO1 or knockout cell lines to ensure reliability. As NQO1 gains attention as a therapeutic target or biomarker, its antibodies remain essential for diagnostic development and mechanistic studies.
×