

| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
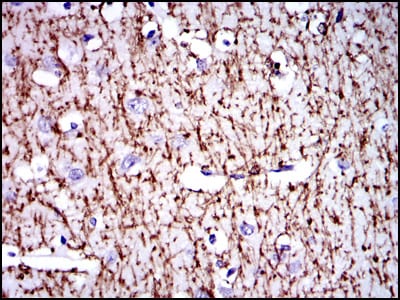
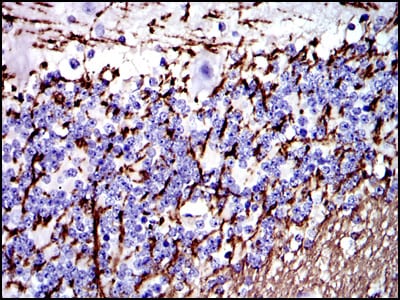
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
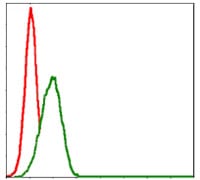
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MGC99675 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4155 |
| clone | 2H9 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human MBP expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于MBP(髓鞘碱性蛋白)抗体的代表性文献,按发表时间排序:
1. **"Antibodies to myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis"**
*Authors: Warren KG, Catz I* (1986)
**摘要**:研究多发性硬化症(MS)患者血清和脑脊液中抗MBP抗体的水平,发现急性复发期患者抗体水平显著升高,提示MBP抗体可能与疾病活动性相关。
2. **"Myelin basic protein-specific autoantibodies in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients are characterized by low-affinity interactions"**
*Authors: Lampasona V, et al.* (1993)
**摘要**:通过免疫印迹和竞争性ELISA分析,发现MS患者的MBP抗体主要为低亲和力IgG型,且与疾病亚型相关,挑战了高亲和力抗体主导自身免疫反应的传统观点。
3. **"Antibody-mediated demyelination in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is dependent on complement activation"**
*Authors: Piddlesden SJ, et al.* (1993)
**摘要**:在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE)模型中,证明抗MBP抗体通过激活补体系统导致髓鞘破坏,揭示了抗体介导的脱髓鞘机制。
4. **"Circulating anti-myelin basic protein antibodies in neurodegenerative diseases: A potential biomarker for axonal damage"**
*Authors: Kuhle J, et al.* (2015)
**摘要**:探讨抗MBP抗体在阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病等多种神经退行性疾病中的检测价值,提出其可能作为轴突损伤的生物标志物,拓展了MBP抗体的临床应用范围。
注:以上为文献核心内容概括,实际引用请核对原文。如需更近期研究(如2020年后),建议检索PubMed等数据库。
Myelin basic protein (MBP) antibodies are autoantibodies targeting MBP, a critical component of the myelin sheath that insulates nerve fibers in the central and peripheral nervous systems. MBP constitutes ~30% of myelin protein and plays a structural role in maintaining compact myelin layers. First identified in the 1970s, MBP antibodies gained attention for their association with demyelinating diseases, particularly multiple sclerosis (MS) and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of MS. In these conditions, immune-mediated attacks on MBP contribute to myelin destruction, disrupting nerve signal transmission.
While early studies suggested MBP antibodies as potential biomarkers for MS, their diagnostic specificity remains limited due to variable detection across patients and overlap with other neurological disorders. Current research focuses on their role in disease mechanisms, including epitope-specific responses and antibody-mediated myelin injury. MBP antibodies are also utilized experimentally to study autoimmune demyelination and evaluate therapeutic interventions. Notably, MBP's high susceptibility to proteolytic degradation and post-translational modifications (e.g., citrullination) influence its antigenicity, complicating antibody detection and clinical correlations. Despite being less emphasized in modern MS diagnostics compared to other targets (e.g., aquaporin-4 or MOG), MBP antibodies remain historically significant in understanding autoimmune neuropathology.
×