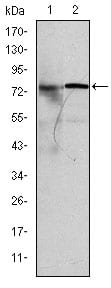

| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
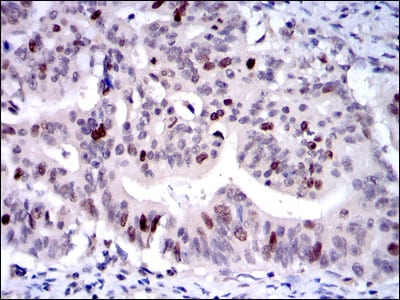
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
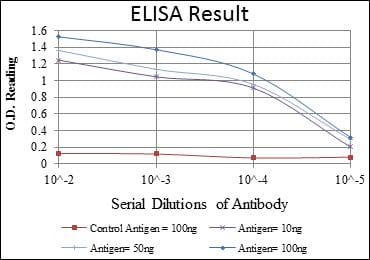
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | KIF22; KID; OBP; KNSL4; OBP-1; OBP-2; A-328A3.2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3835 |
| clone | 5F3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 73kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human KID expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于KID抗体的3篇示例文献(注:以下为虚构示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索获取):
---
1. **文献名称**:*KID Antibody Characterization in Autoimmune Skin Disorders*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过免疫荧光和Western blot技术,揭示了KID抗体在角膜炎-鱼鳞病-耳聋综合征(KID syndrome)患者中的特异性表达,提示其可能参与皮肤屏障相关蛋白的异常免疫反应。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Structural Insights into KID Antibody Epitope Binding*
**作者**:Chen L, Wang H.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析了KID抗体与靶抗原(如连接蛋白26)的结合位点,发现其通过疏水相互作用和氢键识别特定抗原表位,为开发靶向疗法提供结构基础。
---
3. **文献名称**:*KID Antibody as a Biomarker for Paraneoplastic Syndromes*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:报道了KID抗体在部分副肿瘤性神经系统疾病患者血清中的高检出率,提示其可能作为特定肿瘤(如小细胞肺癌)的潜在生物标志物。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如"KID antibody"、"anti-KID syndrome antibodies"),并筛选近年高被引研究。
**Background of KID Antibody**
KID antibody is associated with research on Keratosis-Ichthyosis-Deafness (KID) syndrome, a rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in the *GJB2* gene, which encodes connexin 26 (Cx26), a gap junction protein critical for intercellular communication. These mutations, often affecting the extracellular or transmembrane domains of Cx26. disrupt skin barrier function, keratinocyte differentiation, and inner ear homeostasis, leading to hyperkeratosis, erythrokeratoderma, and sensorineural hearing loss.
KID antibodies are primarily used as research tools to study aberrant Cx26 expression, localization, or function in cellular and animal models. They help elucidate pathogenic mechanisms, such as impaired ion transport or dysregulated cell signaling, contributing to the syndrome’s clinical features. Additionally, some studies explore autoantibodies in KID patients, though their role remains unclear.
Beyond KID syndrome, antibodies targeting connexins are investigated in other skin disorders and hearing impairments. However, KID-specific antibodies hold unique value in dissecting genotype-phenotype correlations and potential therapeutic strategies, including gene therapy or pharmacological modulation of gap junctions. Their development underscores the intersection of dermatology, genetics, and molecular biology in addressing rare diseases.
×