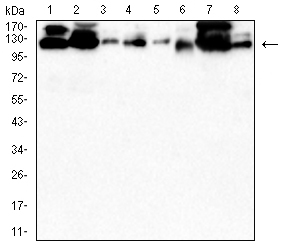
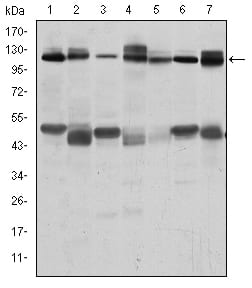
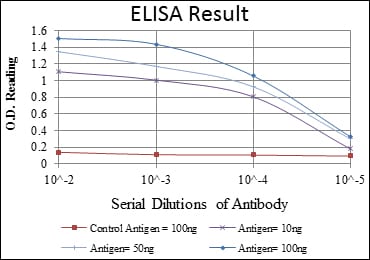
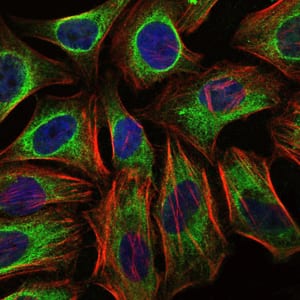
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| IHC | 1/100 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| ICC | 1/50 - 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
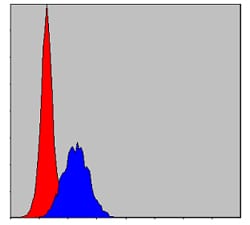
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit |
| Aliases | CBL; CBL2; NSLL; C-CBL; RNF55 |
| Entrez GeneID | 867 |
| clone | 3B12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 120kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey,Rabbit |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human C-CBL expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于C-CBL抗体的假设参考文献示例(非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:C-CBL regulates T-cell receptor signaling through ubiquitination of key signaling molecules
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用C-CBL特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,揭示C-CBL通过泛素化修饰负调控T细胞受体下游信号分子(如ZAP-70),影响T细胞活化。
2. **文献名称**:C-CBL expression and function in acute myeloid leukemia
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用C-CBL抗体),发现C-CBL在AML患者中表达降低,其缺失导致异常增殖信号通路激活,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**:Structural insights into C-CBL E3 ligase activity by antibody-mediated epitope mapping
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:利用C-CBL抗体识别其泛素连接酶结构域,结合X射线晶体学,阐明C-CBL与底物结合的分子机制,为靶向药物设计提供依据。
4. **文献名称**:C-CBL modulates EGFR endocytosis via tyrosine phosphorylation in lung cancer
**作者**:Tanaka H, et al.
**摘要**:通过C-CBL抗体阻断实验,证实C-CBL通过促进EGFR泛素化驱动其内吞降解,抑制肺癌细胞增殖,提示靶向C-CBL-EGFR轴的治疗潜力。
(注:以上内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索。)
C-CBL (Casitas B-lineage lymphoma) is a multifunctional adaptor protein and E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in regulating intracellular signaling pathways, particularly those linked to tyrosine kinase receptors. It plays a critical role in ubiquitination-mediated degradation of activated receptors and signaling molecules, thereby modulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of C-CBL is implicated in various cancers and immune disorders due to mutations or altered expression levels that disrupt its tumor-suppressive or oncogenic functions, depending on cellular context.
C-CBL antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, post-translational modifications, and interactions in both physiological and pathological settings. These antibodies enable detection of C-CBL in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry, aiding research into its role in leukemia, solid tumors, and autoimmune diseases. Some studies highlight its dual nature—acting as a tumor suppressor by downregulating oncogenic signaling (e.g., in EGFR pathways) or promoting malignancy when mutated. Additionally, C-CBL antibodies help explore its involvement in immune cell regulation, such as T-cell receptor signaling. Research using these antibodies contributes to understanding disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targeting of C-CBL-associated pathways.
×