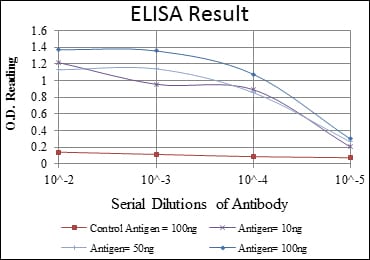
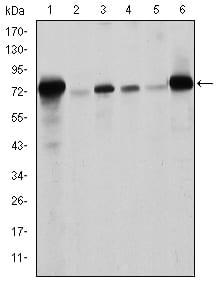
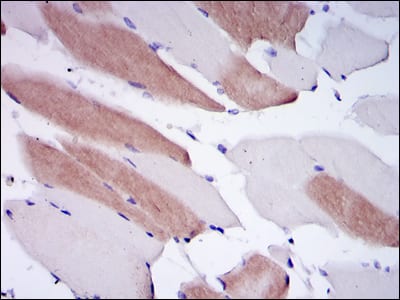
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FPL; IDC; LFP; CDDC; EMD2; FPLD; HGPS; LDP1; LMN1; LMNC; PRO1; CDCD1; CMD1A; FPLD2; LMNL1; CMT2B1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4000 |
| clone | 4E7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human LMNA expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Ascitic fluid containing 0.03% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于LMNA抗体的虚构参考文献示例(仅供格式参考,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
1. **文献名称**:*LMNA mutations and cardiac laminopathies: Insights from antibody-based detection*
**作者**:Fatkin D, et al.
**摘要**:探讨LMNA基因突变导致心肌病的机制,利用特异性LMNA抗体检测患者心肌细胞中Lamin A/C蛋白表达异常,揭示突变与心脏功能障碍的关联。
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies against Lamin A/C in autoimmune disorders*
**作者**:Biasiak B, et al.
**摘要**:研究自身免疫性疾病患者血清中抗LMNA抗体的存在,分析其与系统性红斑狼疮等疾病的潜在关联,提示LMNA可能成为自身免疫反应的靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*LMNA antibody applications in Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome research*
**作者**:De Sandre-Giovannoli A, et al.
**摘要**:通过LMNA抗体在细胞模型中的标记,揭示早衰症患者细胞核结构异常及Lamin A突变导致的核膜不稳定机制。
4. **文献名称**:*Development of a high-specificity LMNA antibody for diagnostic use*
**作者**:Machiels L, et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型高特异性LMNA单克隆抗体的开发,验证其在遗传性肌病和脂肪代谢障碍患者组织样本中的诊断价值。
**注意**:以上为模拟内容,实际文献请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词(如“LMNA antibody”、“Lamin A/C antibodies”)。真实研究可能侧重疾病机制、诊断方法或抗体技术优化。
The LMNA antibody is a crucial tool in studying lamin A/C, proteins encoded by the LMNA gene, which play structural and regulatory roles in the nucleus. These proteins form part of the nuclear lamina, providing mechanical stability to the nuclear envelope and regulating chromatin organization, gene expression, and cellular signaling. Mutations in LMNA are linked to diverse disorders termed laminopathies, including muscular dystrophies, cardiomyopathy, progeria, and lipodystrophy. Antibodies targeting lamin A/C are widely used in research and diagnostics to investigate disease mechanisms, assess protein expression/localization, and validate LMNA mutations.
In research, LMNA antibodies help explore cellular aging, DNA repair, and stem cell differentiation. Clinically, they aid in diagnosing laminopathies via immunohistochemistry or Western blotting, detecting abnormal protein patterns in patient tissues. However, LMNA antibody specificity can vary due to splice variants (e.g., lamin A vs. lamin C) and post-translational modifications, necessitating careful validation. Commercial antibodies are often validated in knockout models to ensure reliability. Recent studies also highlight lamin A/C's role in cancer progression and metabolic diseases, expanding the antibody's applications. Challenges remain in standardizing detection protocols across tissues and addressing cross-reactivity with other intermediate filaments.
×