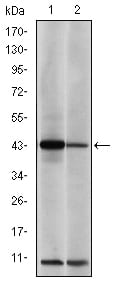

| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
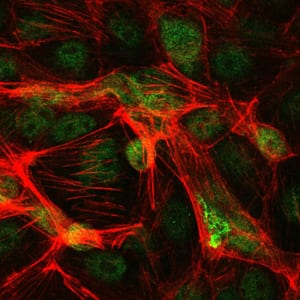
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
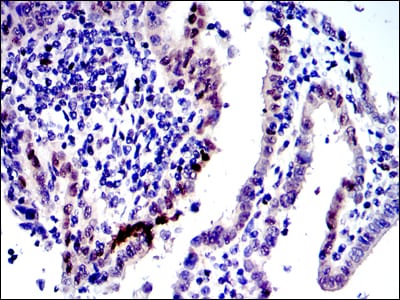
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
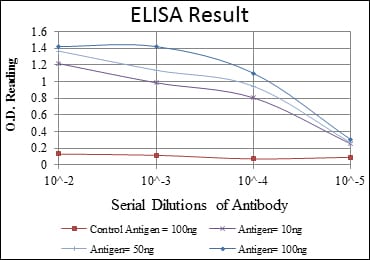
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Aliases | AP1; AP-1; c-Jun; Jun |
| Entrez GeneID | 3725 |
| clone | 5B1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human c-Jun expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于c-Jun抗体的3篇参考文献(简要概括内容):
1. **"Identification and characterization of a c-Jun antibody for functional studies in AP-1 signaling pathways"**
- **作者**: Angel P., Karin M.
- **摘要**: 该文献描述了针对c-Jun蛋白N末端结构域的单克隆抗体的开发与验证,证实其在免疫沉淀和Western blot中特异性识别c-Jun,并应用于研究AP-1复合物在细胞应激反应中的调控机制。
2. **"c-Jun phosphorylation by JNK regulates its transcriptional activity in response to oxidative stress"**
- **作者**: Davis R.J., Dérijard B.
- **摘要**: 研究利用c-Jun抗体(克隆KM-1)通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示JNK激酶介导的c-Jun磷酸化对其转录活性的影响,证明其在氧化应激条件下促进靶基因表达的作用。
3. **"Differential expression of c-Jun in neuronal apoptosis: validation of a specific antibody for immunohistochemistry"**
- **作者**: Ham J., Eilers A.
- **摘要**: 验证了一种兔源多克隆c-Jun抗体的特异性,通过敲除实验和免疫组化分析,证明其在检测神经元损伤模型中c-Jun蛋白表达上调的可靠性,并关联其与凋亡通路的激活。
c-Jun, a key component of the AP-1 transcription factor complex, is a proto-oncoprotein involved in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and stress responses. It dimerizes with other Jun/Fos family members (e.g., c-Fos) to bind DNA and modulate gene expression. c-Jun is activated via phosphorylation (e.g., at Ser63/Ser73 by JNK kinases) in response to growth factors, cytokines, or cellular stress, making it a critical mediator in MAPK signaling pathways.
c-Jun antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and activation status in biomedical research. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting (WB), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect endogenous c-Jun or its phosphorylated forms. Specific clones (e.g., recognizing total c-Jun or phospho-Ser63/73) enable differentiation between inactive and activated states, providing insights into cellular signaling dynamics. Validated c-Jun antibodies are critical for investigating its role in cancer (e.g., tumor progression, drug resistance), neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammatory conditions. Many antibodies are raised against epitopes in the N-terminal transactivation domain or C-terminal DNA-binding domain, with host species (rabbit, mouse) and clonal specificity (monoclonal/polyclonal) varying by application. Knockout-validated antibodies ensure reliability in distinguishing c-Jun from homologous proteins. Their applications extend to drug development, as c-Jun is a potential therapeutic target in diseases driven by dysregulated AP-1 activity.
×