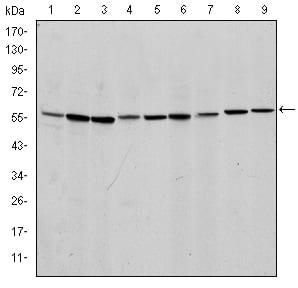
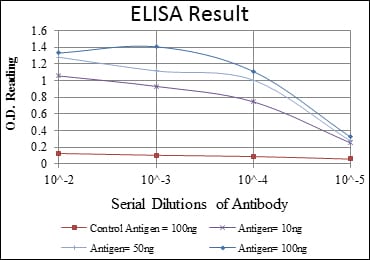
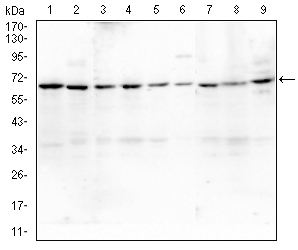

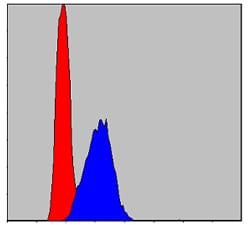
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,,Monkey |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat,,Monkey |
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,,Monkey |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,,Monkey |
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat,,Monkey |
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat,,Monkey |
| Aliases | AIFM1; AIF; PDCD8; COXPD6; MGC111425 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9131 |
| clone | 4E7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 67kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,,Monkey |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human AIF expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于AIF抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor*
**作者**: Susin, S. A., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆并鉴定了AIF蛋白,证明其从线粒体释放至细胞核可触发凋亡,实验中利用AIF抗体验证其亚细胞定位及功能,为后续凋亡机制研究奠定基础。
2. **文献名称**: *Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death*
**作者**: Joza, N., et al.
**摘要**: 通过构建AIF缺陷小鼠模型,结合AIF抗体检测,发现AIF缺失导致胚胎致死及神经细胞凋亡异常,证实AIF在发育和细胞程序性死亡中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**: *Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a key regulator of apoptotic and necrotic neural cell death*
**作者**: Cheung, E. C., et al.
**摘要**: 研究AIF在脑缺血中的角色,使用AIF抗体揭示其在缺氧时从线粒体转位至细胞核的过程,并关联其与坏死性细胞死亡的调控机制。
---
这些文献涵盖了AIF抗体的基础研究、功能验证及疾病模型应用,适用于凋亡机制和实验方法参考。
**Background of AIF Antibody**
The Apoptosis-Inducing Factor (AIF) is a mitochondrial flavoprotein with dual roles in cellular homeostasis and apoptosis. Initially identified for its involvement in caspase-independent programmed cell death, AIF translocates from mitochondria to the nucleus under apoptotic stimuli, triggering chromatin condensation and DNA fragmentation. Beyond apoptosis, AIF is critical for maintaining mitochondrial structure, bioenergetics, and redox balance, supported by its role in regulating respiratory chain complexes.
AIF antibodies are essential tools in studying these processes. They enable detection of AIF’s subcellular localization (e.g., via immunofluorescence) and expression levels (e.g., via Western blot), helping to dissect its pro-apoptotic versus pro-survival functions. Research using AIF antibodies has revealed its involvement in neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s), ischemic injuries, and cancer, where AIF dysregulation correlates with pathological outcomes.
Structurally, AIF antibodies often target conserved epitopes, such as the N-terminal mitochondrial localization signal or C-terminal DNA-binding domain. Some antibodies distinguish between full-length AIF (∼67 kDa) and its truncated forms, which arise during apoptosis. The development of selective AIF antibodies has advanced therapeutic exploration, including strategies to inhibit AIF-mediated apoptosis in neurodegeneration or enhance its pro-death role in cancer. Overall, AIF antibodies remain pivotal in unraveling the multifaceted biology of AIF and its translational potential.
×