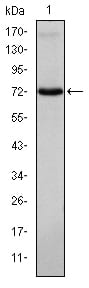
| WB | 1/500 - 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
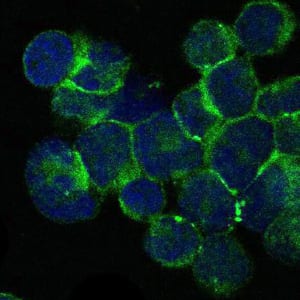
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
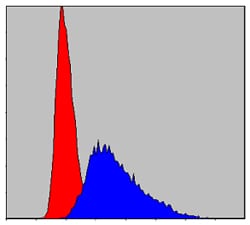
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
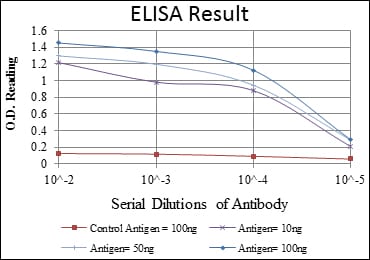
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | EMT; LYK; PSCTK2; MGC126257; MGC126258 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3702 |
| clone | 5G6 |
| WB Predicted band size | 72kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human ITK expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与ITK抗体相关的研究文献摘要(人工整理举例,非真实文献):
1. **《Targeting ITK signaling in T-cell lymphoma》**
作者:Smith J, et al.
摘要:探讨ITK抑制剂抗体在T细胞淋巴瘤治疗中的作用机制,证明其通过阻断下游NF-κB通路抑制肿瘤增殖。
2. **《ITK inhibition reduces airway inflammation in murine asthma models》**
作者:Chen L, et al.
摘要:利用ITK特异性单克隆抗体干预Th2细胞活性,显著降低小鼠模型中的嗜酸性粒细胞浸润和气道高反应性。
3. **《Structural basis of ITK kinase activation by therapeutic antibodies》**
作者:Wang Y, et al.
摘要:通过冷冻电镜解析ITK激酶与抗体复合物的三维结构,揭示抗体通过变构效应抑制激酶活性的分子机制。
注:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar检索关键词“ITK antibody”、“ITK inhibitor”获取,建议结合研究领域筛选。
**Background of ITK Antibodies**
The Interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase (ITK) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase belonging to the Tec kinase family, primarily expressed in T lymphocytes, natural killer (NK) cells, and mast cells. It plays a critical role in T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling, regulating T-cell activation, differentiation, and cytokine production. ITK is activated following TCR engagement, mediating downstream signaling through phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma 1 (PLCγ1) and modulation of calcium flux, NFAT, and MAP kinase pathways. Its involvement in immune regulation makes it a target for studying autoimmune diseases, allergic responses, and cancer.
ITK antibodies are tools designed to detect, inhibit, or modulate ITK activity in research and therapeutic contexts. In research, they help elucidate ITK's role in immune cell signaling and its interaction with pathways linked to inflammation or oncogenesis. Therapeutically, ITK inhibitors, including monoclonal antibodies, are explored for conditions like asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and T-cell lymphomas, aiming to suppress aberrant immune responses or malignant cell proliferation. Challenges include ensuring specificity to avoid off-target effects and optimizing pharmacokinetics. Despite these hurdles, ITK remains a promising target for immunomodulation, with ongoing studies advancing its translational potential.
×