| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
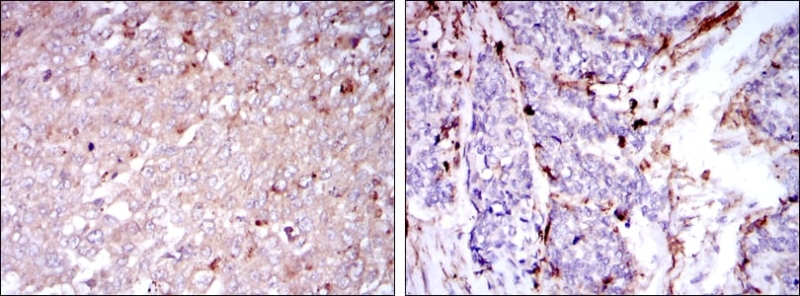
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
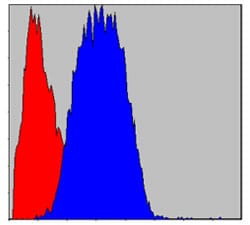
| FCM | 1/200 - 1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
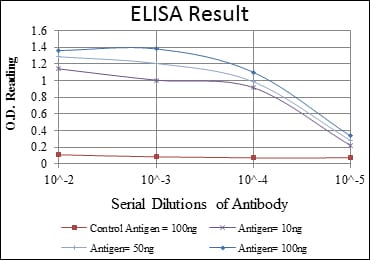
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RP41; AC133; CD133; MCDR2; STGD4; CORD12; PROML1; MSTP061 |
| Entrez GeneID | 8842 |
| clone | 3F10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 133kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of human CD133. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于CD133抗体的代表性文献,按标准格式整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells
**作者**:Singh SK, et al.
**摘要**:首次证明CD133抗体可用于分离脑肿瘤干细胞,CD133+细胞具有更强的肿瘤形成能力和自我更新特性,揭示了其在胶质母细胞瘤中的作用。
2. **文献名称**:Distinct populations of cancer stem cells drive tumor growth and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer
**作者**:Hermann PC, et al.
**摘要**:利用CD133抗体筛选胰腺癌干细胞,发现CD133+细胞亚群在肿瘤增殖和转移中起关键作用,并与化疗耐药性相关。
3. **文献名称**:CD133 expression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis
**作者**:Wang S, et al.
**摘要**:通过荟萃分析评估CD133抗体在结直肠癌中的临床应用,证实CD133高表达与患者预后不良及转移风险显著相关。
4. **文献名称**:Isolation and characterization of CD133+ stem cells from human liver tumors
**作者**:Yin S, et al.
**摘要**:开发基于CD133抗体的流式分选技术,成功分离肝癌干细胞,并验证其在体外和体内模型中的致瘤潜能。
---
以上文献涵盖了CD133抗体在肿瘤干细胞鉴定、分选及临床应用中的关键研究。如需具体DOI或期刊年份,可进一步补充。
CD133. also known as Prominin-1. is a transmembrane glycoprotein widely recognized as a surface marker for stem and progenitor cells. Identified in the 1990s, CD133 is characterized by five transmembrane domains and extracellular N-glycosylation sites, which contribute to its role in membrane organization and cellular interactions. It is expressed in various stem cell populations, including hematopoietic stem cells, neural stem cells, endothelial progenitors, and cancer stem cells (CSCs).
CD133 antibodies were developed to target specific extracellular epitopes of the protein, enabling the identification, isolation, and characterization of CD133⁺ cells. These antibodies (e.g., clones AC133. AC141) have become essential tools in cancer research, as CD133⁺ CSCs are implicated in tumor initiation, therapy resistance, and metastasis. In regenerative medicine, CD133 antibodies aid in isolating stem cells for therapeutic applications.
Notably, CD133 glycosylation patterns vary across cell types and disease states, influencing antibody binding specificity. For instance, the AC133 epitope is lost upon cell differentiation, highlighting its utility in distinguishing undifferentiated cells. However, discrepancies in antibody performance across experimental conditions (e.g., fixation methods) necessitate careful validation.
Despite challenges, CD133 antibodies remain pivotal in advancing stem cell biology, cancer therapeutics, and biomarker studies, underscoring their dual role in research and clinical translation.
×