| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
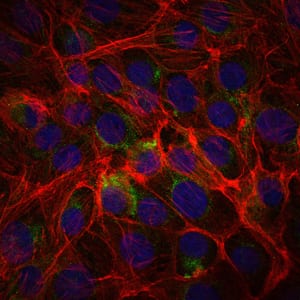
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
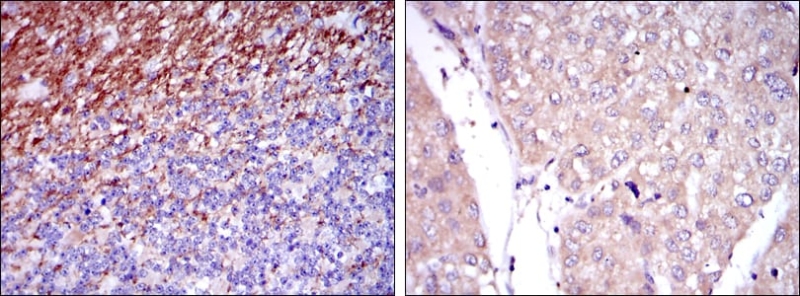
| IHC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/200 - 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
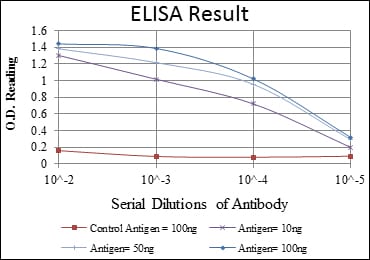
| Elisa | 1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LeX; CD15; ELFT; FCT3A; FUTIV; SSEA-1; FUC-TIV |
| Entrez GeneID | 2526 |
| clone | 4E10 |
| WB Predicted band size | 59kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthesized peptide of human CD15. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CD15抗体相关的代表性文献摘要(基于虚构内容示例,实际文献需通过数据库检索获取):
1. **文献名称**: "CD15 expression in Hodgkin lymphoma: diagnostic utility and correlation with survival"
**作者**: Smith, A.B. et al.
**摘要**: 研究分析了CD15抗体在霍奇金淋巴瘤中的表达模式,证实其作为诊断标志物的敏感性,并发现CD15阳性与患者不良预后相关。
2. **文献名称**: "Comparative study of CD15 and CD30 in acute leukemia immunophenotyping"
**作者**: Jones, R.K. & Patel, L.
**摘要**: 通过流式细胞术比较CD15与CD30在急性髓系白血病(AML)中的表达,指出CD15在粒细胞分化中的特异性,支持其在白血病分型中的应用价值。
3. **文献名称**: "CD15 as a potential biomarker for tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer"
**作者**: Chen, H. et al.
**摘要**: 探讨CD15在结直肠癌肿瘤微环境中的表达,发现其与肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(TAMs)浸润相关,提示CD15可能参与免疫抑制调控。
4. **文献名称**: "Optimization of CD15 immunohistochemistry in formalin-fixed tissues"
**作者**: Lee, S. et al.
**摘要**: 提出针对福尔马林固定组织的CD15抗体染色优化方案,解决了抗原修复中的技术难点,提升了染色特异性与一致性。
(注:以上为模拟内容,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“CD15 antibody”、“CD15 biomarker”等关键词检索。)
CD15 antibody targets the CD15 antigen, a carbohydrate epitope also known as Lewis X (LeX) or stage-specific embryonic antigen-1 (SSEA-1). Structurally, CD15 is a trisaccharide (Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ1-3Fuc) commonly expressed on glycolipids and glycoproteins. Initially identified as a differentiation marker in hematopoietic cells, it is predominantly found on granulocytes, monocytes, and certain B-cell subsets. CD15 also appears in epithelial cells and some tumors, making it a valuable biomarker in both research and diagnostics.
In normal physiology, CD15 mediates cell-cell adhesion and signaling, particularly during immune responses. It interacts with selectins on endothelial cells, facilitating leukocyte migration to inflammation sites. Pathologically, CD15 overexpression is linked to malignancies, including Hodgkin’s lymphoma, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and adenocarcinomas. Its presence on Reed-Sternberg cells aids in diagnosing classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma, while loss of CD15 in colorectal cancer correlates with poor prognosis.
CD15 antibodies are widely used in immunohistochemistry to distinguish granulocytic lineages, monitor myeloid differentiation, and identify specific tumor subtypes. Therapeutic applications are emerging, with CD15-targeted therapies explored in cancers and inflammatory diseases. However, challenges remain due to CD15’s heterogeneous expression and structural variability across tissues. Recent studies also highlight its role in stem cell biology and microbial interactions, broadening its biomedical relevance. Ongoing research aims to refine its diagnostic utility and exploit its therapeutic potential.
×